Startups usually run at a deficit while designing and building the product. But companies are designed to make money, and over time, as unit economics and customer acquisition costs improve, you’ll probably tip into the blue. Maybe. Hopefully.
At the very least, that’s what your investors will be betting on. So that means your business model slide needs to paint a picture that shows where you’re at now and how the business can grow over time.

In theory, your “business model” could include every aspect of the business; the Business Model Canvas is one way to explore that, and you could easily spend an hour just talking about the whole end-to-end business model. For the purposes of a funding pitch, however, it’s likely you only need a few crucial elements:
- COGS, or cost of goods sold, is the incremental cost for each unit you deliver. For software, this typically rounds to zero, but for hardware products or more service-driven businesses, the unit cost can be substantial.
- CAC, or customer acquisition cost, is the cost of sales and marketing divided by how many customers you’ve signed up.
- LTV, or lifetime value: How much is each customer worth, on average, once you sign them up?
- R&D cost is what it costs to develop the product. This isn’t usually included in the business model, but if the cost of R&D is astronomical and the cost-to-profit line never intersects, you could have a problem worth exploring.
- The pricing model isn’t usually part of the business model itself (it falls under LTV), but if you’re doing something unusual or creative with your pricing, it’s worth including that, either here or on your go-to-market slide.
Breaking those numbers down and presenting them the right way can greatly benefit how you tell your startup’s story to investors.
Customer acquisition cost
Whatever your strategy is for getting customers into and through your acquisition funnel, it probably costs money. Some companies advertise directly, some advertise using influencers, others go to trade shows. There are tons of ways to find new customers; some channels will be more expensive, and if you’re lucky, some can even be free.
As a business, it’s important to have a firm grasp on what all your acquisition channels are and what they cost. I’ll touch on this more down below, but for a business model slide to make sense, you probably need to report your blended CAC.
A quick note here: “Our growth is organic” or “We haven’t spent a penny on marketing” are not what investors want to hear. Yes, it’s impressive, but those customer channels can’t be scaled rapidly, and if you suddenly find yourself with a $30,000-per-month marketing budget, you won’t know where to deploy cash to grow faster.
Lifetime value
If you make one-off sales, your lifetime value is the value of the sale. That goes for things like televisions: People buy a TV and don’t have the need for another one for at least another decade.
But even rare, one-off purchases can have a surprisingly high LTV if you’re able to build a relationship. If you are a car salesperson selling a new car, you might, for example, be able to add on service contracts, which encourage customers to come back.
For SaaS and subscription businesses, LTV is where it’s at: How long can you retain customers, and what’s their average spend? Can you upsell or cross-sell to them, which would increase the LTV?
The only time you know a customer’s actual lifetime value is when they stop being a customer. For some businesses, a customer ending the relationship with you is a positive thing; a good example of this would be a dating site, where success is measured by how many people don’t return because they’re settled in happy relationships.
But a customer ending a relationship with you is something you typically want to avoid. So in order to figure out a customer’s lifetime value, you need to make a calculated guess about how long each customer will stay around and what their spending patterns are. At the beginning of a startup’s journey, this will be little more than qualified guesswork. But as the business grows, you’ll start to notice patterns and customer habits that could make it easier to build more sophisticated models that get a better approximation for LTV.
This might be obvious but still worth mentioning: If your LTV is lower than your CAC, you have a serious problem. The same is true if the numbers more or less match; if you’re not making a per-customer profit, you’ll eventually run out of cash because the R&D and operations of the business will continue to incur costs.
Your CAC-to-LTV ratio is important to investors. If your customers spend $10 to every $1 you spend on acquiring them, you should spend as much money as you can to acquire as many customers as you can.
Some companies choose not to report their LTV because they’re uncomfortable trying to model five or six years’ worth of customer behavior. Instead, they try to report average first-year spend and ensure that the customer acquisition cost is covered in that first year. The assumption is that if you manage to hang onto your customer beyond that first year, it’s essentially pure profit.
Cost of goods sold
COGS can vary wildly from company to company, depending on the market and industry. Delivering a purely software-as-a-service product can often be done very cheaply, and the COGS rounds to zero. For other products that are more server-intensive (for example, if you have to run complex AI models that take up a lot of processing power, or if you have to transcode and send large volumes of video content), the cost of delivery can be significantly higher.
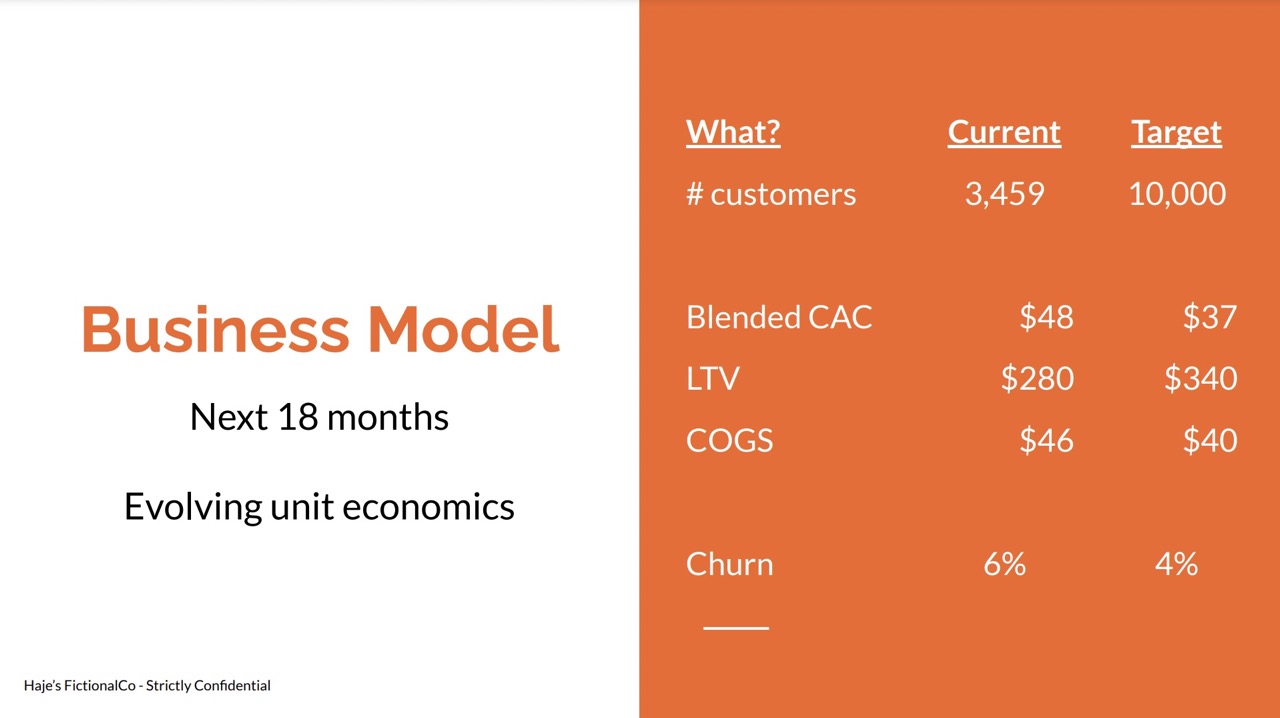
One way to present the business model is to show a snapshot of what is currently true in the business as well as which numbers you’re working toward. You can dig deeper into this in the operating plan section, but it’s helpful to be able to talk about specific goals and how you’re planning on getting there.
It’s hard to give generalized advice about how you treat COGS as part of a pitch, but as a rule of thumb, if your COGS is less than 10% of your revenue, you can probably ignore it as part of the pitch. If your contribution margins are relatively slim, you’ll want to include COGS as part of the conversation because you’ll probably make it a priority to drive the cost of delivering your product or service down.
R&D
R&D often comes at a significant cost, but for the sake of this particular slide, ignore it. A company’s business model, in the context of a funding pitch, is largely about the per-customer cost and revenue, and possibly the unit economics.
R&D is usually a different part of a startup’s story; it’s itemized differently, and most companies don’t amortize their R&D as part of their unit economics. Your R&D costs will show up in your operating plan, so don’t be tempted to confuse the story at this point.
Pricing model
Your pricing model is how you charge your customers. If you’re selling hardware, it’s often the cost of the widget, plus potentially a subscription model for any software powering it. If you’re creating a SaaS business, you’ll probably have a per-business or per-user pricing model, and possibly different tiers, depending on the needs of the customer. Other businesses may have sign-up fees, service contracts, retainers, installation costs or any number of ways to get paid.
For a lot of early-stage companies, the pricing model is pretty straightforward, and it should be; it’s unlikely that your core contribution to the market is innovation on complicated pricing models. As the business grows and the customer base evolves, it would make sense to charge extra for features that unlock greater value for certain customer segments.
For your pitch deck, the rule is simple: Include a pricing model if you really think it needs explaining.
Putting it all together
As part of our Pitch Deck Teardowns, we have a whole bunch of great examples of business models. Here are a few examples:
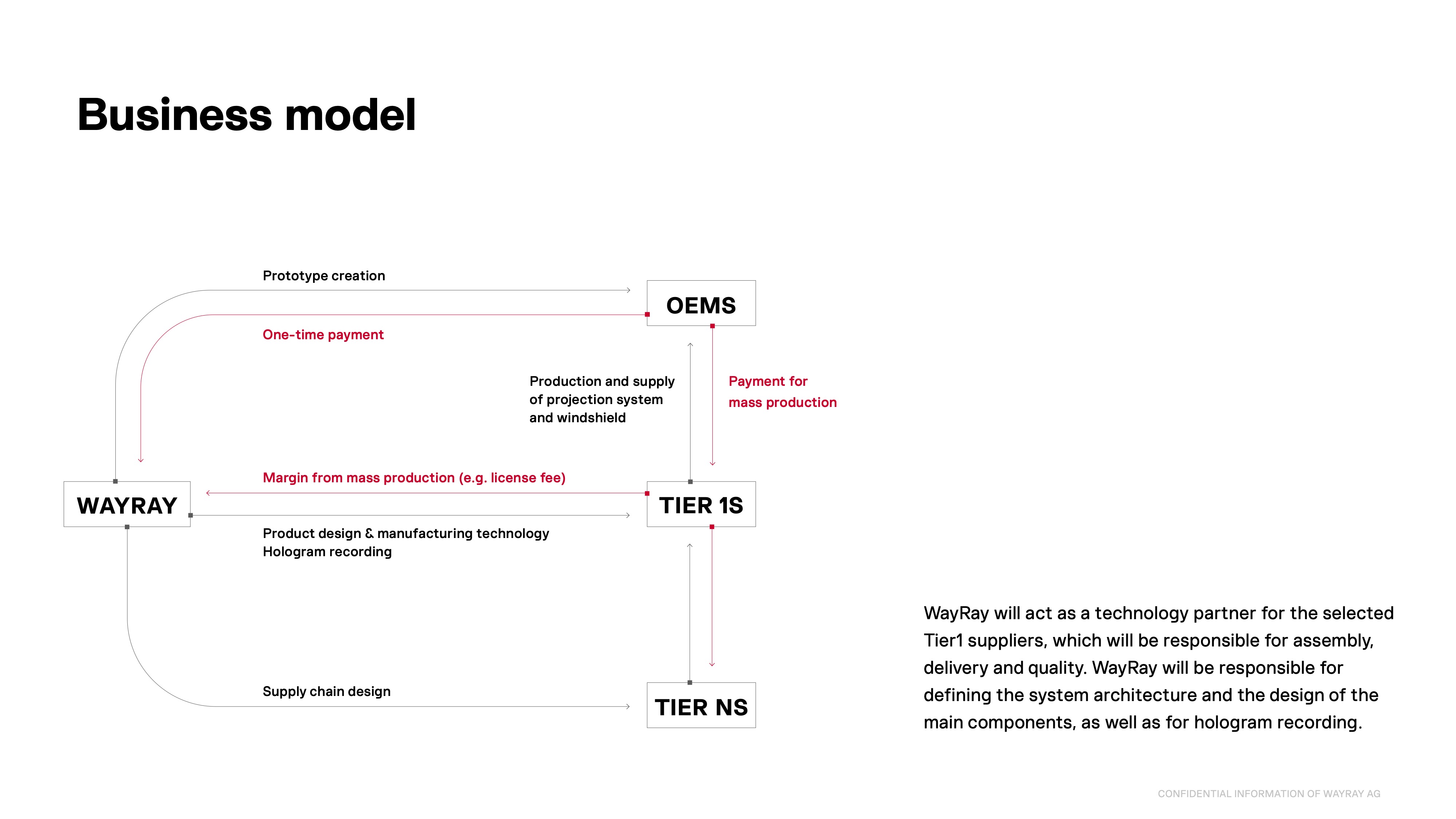
WayRay had a very complicated, 75-slide deck that went into a lot of detail for its $80 million Series C. The business model for the company is complex enough that it warrants a more in-depth explanation. I’d have loved to see how much money is flowing here (for the mass production, one-type payments and license fees), but having an explanation slide is helpful in this case.

For its $15 million Series B, Minut shows a vastly simpler pricing model: subscriptions with two tiers. That’s it — no frills, no confusion. I’d have loved to see more details here, but instead, the company includes some of its important business model data in the KPIs section:
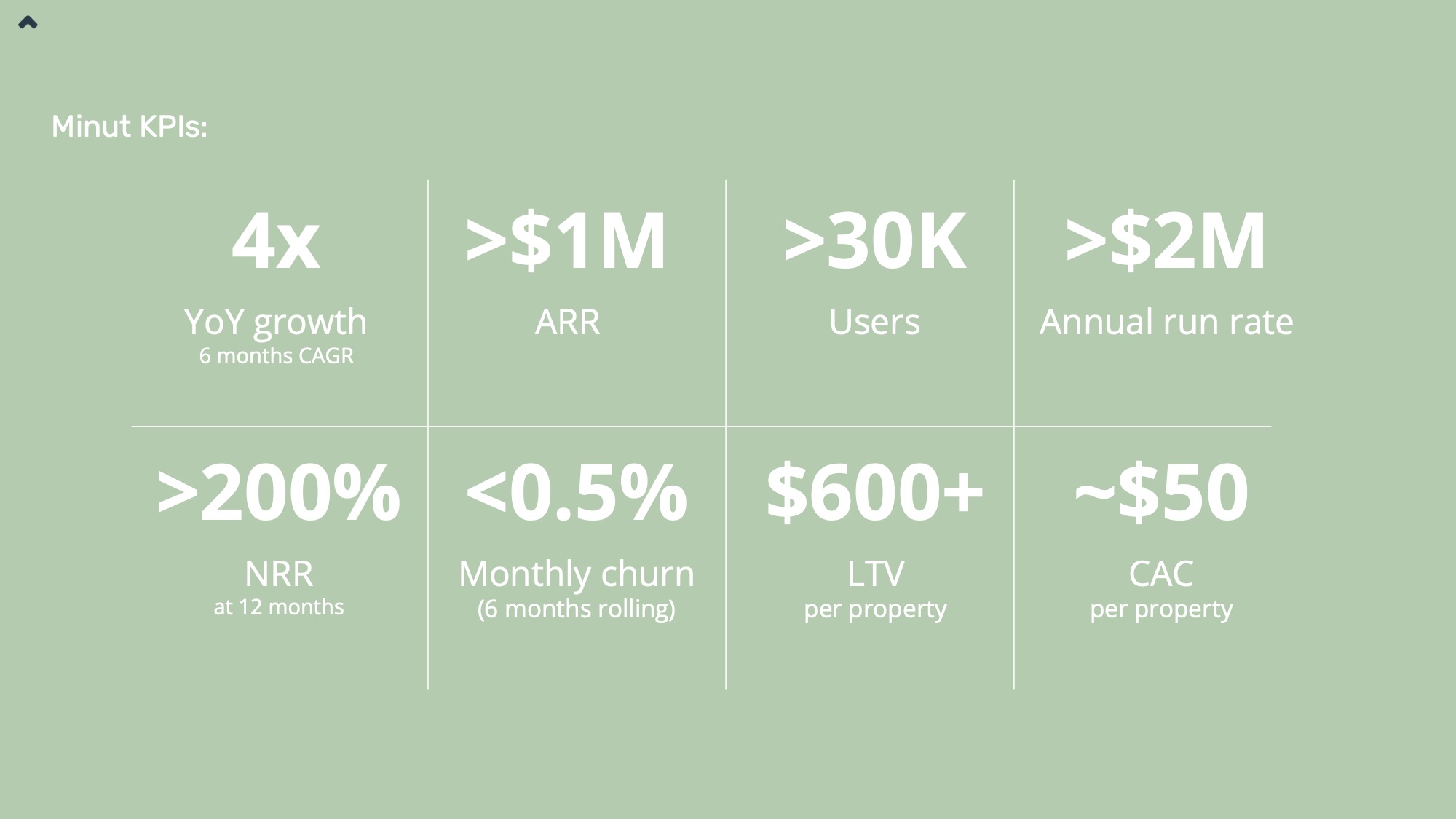
Showing off the churn, LTV and CAC in the KPIs help form a fuller picture of the business model Minut operates with. It works great in this case.
Finally, one of my favorite business model slides came from Orange:

Orange’s business model slide is near perfect. It shows all the important data an investor needs to get a full grasp of the business model dynamics of the company: unit costs, CAC, LTV and CAC:LTV ratio. Beautiful.
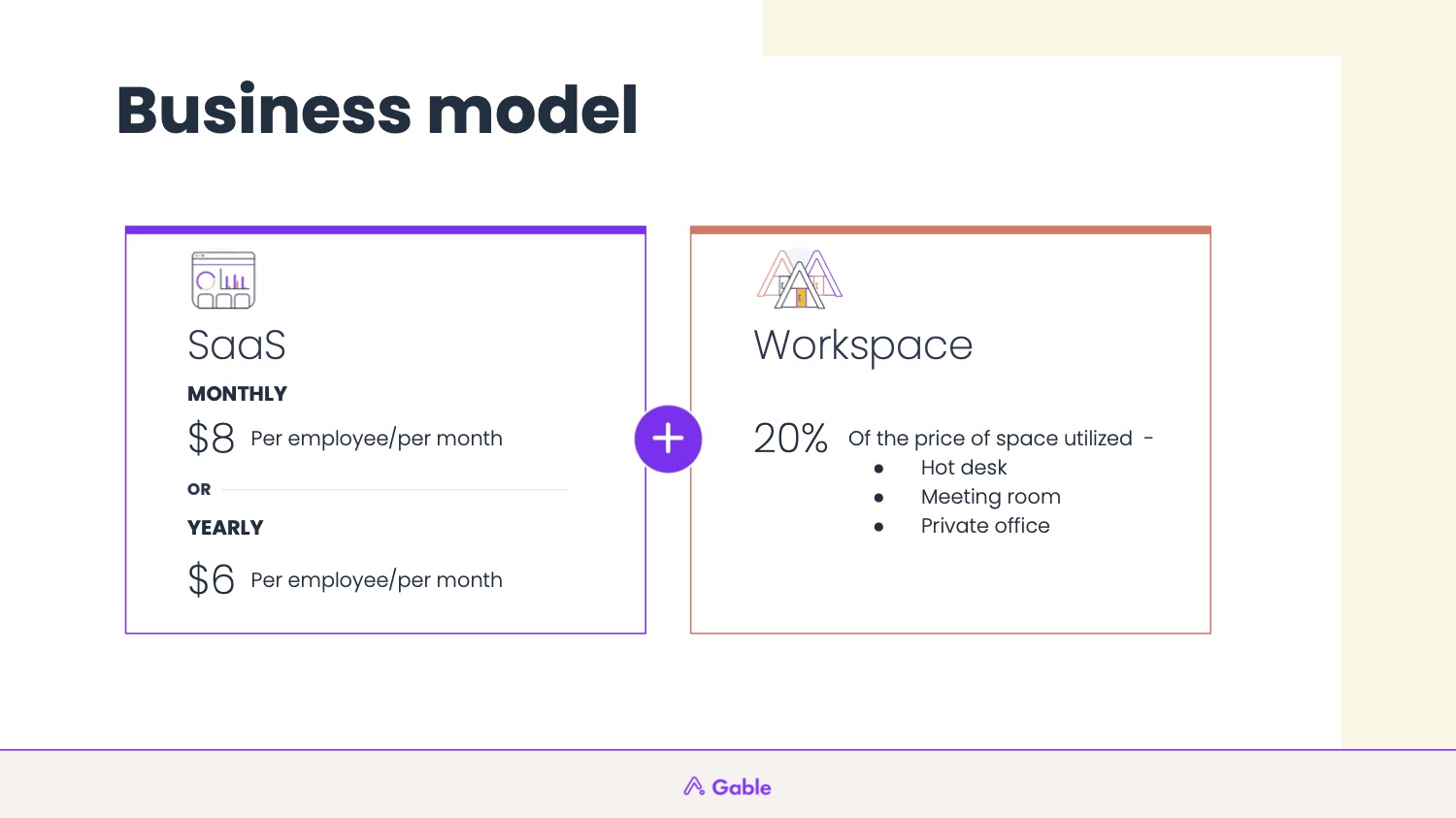
Gable’s business model is a perfect example of how you can keep things simple – even for a company that’s pretty complex.































Comment