Jake Jolis
We recently invested in a team of co-founders who had voluntarily made their own vesting longer than four years. Four-year vesting is the industry standard. Why would someone voluntarily make it longer for themselves?
Their answer: “These days, with companies taking seven to 10 years to reach exit, it would make sense for founders to be on a similar schedule.”
This matters because the four-year co-founder vesting schedule frequently harms startup founders’ interests. Sometimes it damages their startup irreparably.
A growing number of founders are starting to realize this. I talked to quite a few about this over the last two years. Mostly, the “longer-than-four-years-
Importantly, this group of founders assumes they are going to be the ones actually building the company. They created the company. They are the company. Nobody is forcing them out. I suspect founders who already believe this about their own startup will find this post most helpful.
Given the massive implications of co-founder vesting schedules, all startup founders should consider co-founder vesting lengths more carefully and then choose what makes sense for them. You make this decision around the time of incorporation but feel the effects over the lifetime of your company.
4-year vesting schedules are anachronistic
As far back as the 1980s, the standard startup vesting schedule was four or five years, with five being more prevalent on the East Coast. Nobody seems to remember a time it was anything different. The closest I’ve gotten to a logical answer on why it’s four years today stretches back to a pre-401(k) era, from before Reagan’s tax reforms in the ’80s. Prior to then, tax rules incentivized big company pension plans to have vesting periods of at least five years.
Startups didn’t offer traditional pension plans. Instead, startups offered employees stock, vesting over four years instead of five as a competitive move. That is all moot today. It has no relevance for startup founders in 2020.
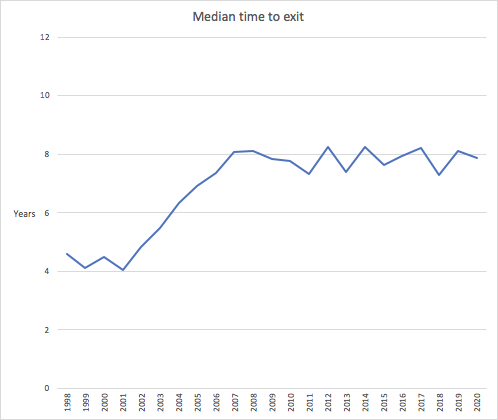
More relevantly, time from founding to exit has gone from four years in 1999 to eight years in 2020. Yet founder vesting remains stuck at four. This is dangerous.
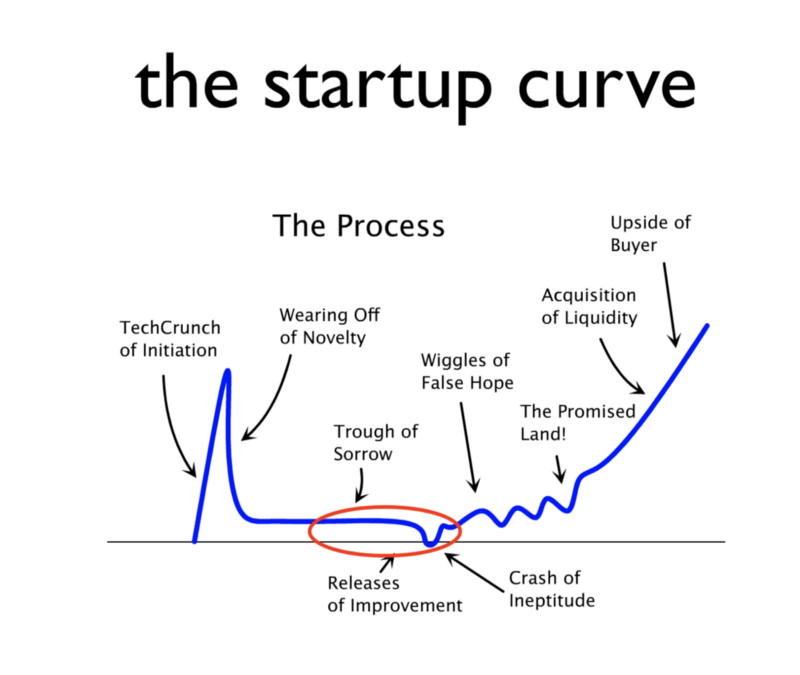
Hedging against the crash of ineptitude
The problem occurs in co-founding teams of two or three equal or near-equal co-founders, when one of them departs in year two or year three and an exit is nowhere in sight. These early-inning departures are extremely common. Usually, they happen during the phase represented by the red oval below:
Let’s go through one example. Needless to say, there are an infinite number of scenarios possible. And yet, the following one is common.
We begin with a first-time founder duo — co-founder A and co-founder B. They split the equity equally, 50-50, on a four-year vesting schedule.
At inception, they both feel a 50-50 split is fair. They don’t put much thought into the vesting schedule, or they think something like: “Even if my co-founder leaves, I’ll still be on track to own my full grant. A quitting co-founder won’t be leaving with any of my equity. So I’m protected.”
- A year in, the startup raises a seed round, selling 20% of their company, inclusive of any accelerators they may have sold equity to.
- As part of the terms, they create a 10% option pool to hire employees.
- A year and a half later, i.e., 2.5 years from inception, co-founder B leaves.
Here’s what the cap table looks like:
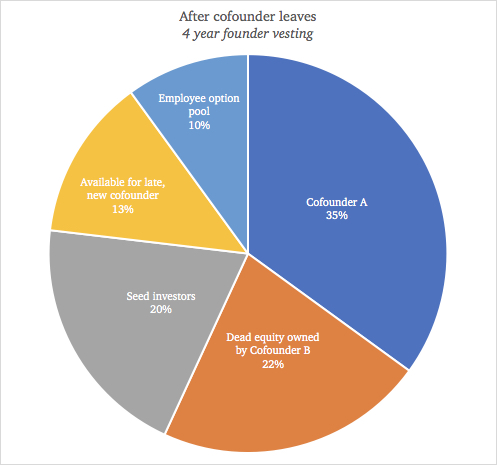
Per their vesting clause, co-founder B walks away with 22% of the cap table.
This equity owned by a departed co-founder is referred to as “dead equity.”
Dead equity is demoralizing. Even though co-founder A agreed to the vesting terms back at the time of inception, they feel differently now. “Why should co-founder B keep so much upside while I’m doing all the work for years to come?” A period of resentment about contribution:reward ratios follows.
2 Kindred Capital partners discuss the firm’s focus and equitable venture model
Setting emotions aside, co-founder A has another problem. The rational way to think about the departed 22% is in terms of the opportunity cost of the dead equity.
The opportunity cost of dead equity is talent and capital. Compensating talent and raising capital are the (only) two things you can use your startup’s equity for, and you need to do both in order for your company to grow large. If you want to build a big business, the road ahead is still long and windy, and you’re going to need every bit of help you can get. If your competitors don’t have dead equity you’re literally competing with a handicap.
For this reason, VCs don’t like to invest in early startups with a lot of dead equity.
In our example, co-founder A tries to attract a “late co-founder” to replace the co-founder B, but only 13% of the cap table is available for this. As soon as the late co-founder candidate sees the cap table, they become painfully aware that their ownership pales in comparison with co-founder B’s.
How to remedy
If instead co-founder A and B had agreed to an eight-year schedule, co-founder B would leave with 11%.
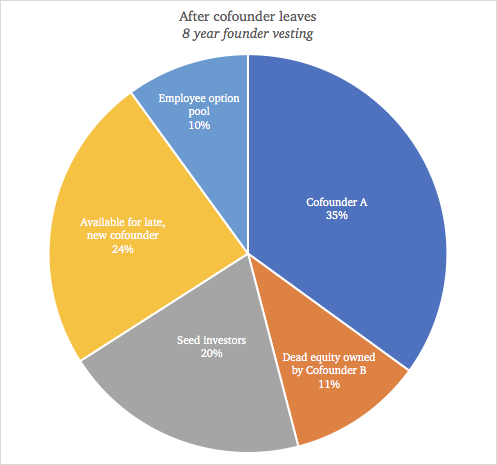
Given the risks still ahead of the business, this level of compensation is often much more fair from a value-creation standpoint. With less dead equity on the cap table, the startup is still attractive in the eyes of VCs and well-positioned to attract a strong co-founder replacement to take the company forward. The alternative can cripple the company, and even co-founder B won’t be happy owning a larger percent of zero.
While it’s better to do it when you start the company, a co-founder unit can elongate their vesting later on as well. The main requirement is that all the co-founders believe it’s in their best interest and agree to it.
Most repeat founders I’ve talked to agree that four years is too short. Personally, if I started another company, I’d pick something like eight. You definitely don’t need to. You might decide four or six is better for your co-founder unit and your company.
But try to think about what would feel fair if the journey were eight years long, since that is indeed what it takes to build something big.
Note: You can keep employees on four-year vesting to be competitive with the rest of the hiring market. This post limits its vesting suggestions to co-founders.
Learning how to ask questions is an essential skill for startup founders






























Comment