Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S., but the healthcare industry spends more money helping patients after they get sick, instead of keeping them healthy.
To fill this gap, Heartbeat Health, founded by Dr. Jeff Wessler, has raised more than $30 million, developing a digital data layer that uses telemedicine, remote diagnostics and digital heart health programs to give patients and clinicians a more proactive way to stay healthy.
On our last episode of TechCrunch Live, we spoke with Wessler and Kindred Ventures’ Kanyi Maqubela to learn how its first fundraising deal came together and how Heartbeat’s pitch deck helped convince Kindred to invest.
Insight versus experience
“We look for founders who have a combination of domain insight and domain experience,” said Maqubela. “A lot of people who are very experienced in a domain are not totally insightful about it. They know all the reasons why you can never do something in that area. It takes a beginner’s mind, almost a little naivety, to have real insight in some areas.”
Though it’s often seen as an advantage to have experience in the industry you’re trying to solve for, or sell to, that experience must be paired with the insight to see a solution.
Maqubela said Wessler’s optimism about addressing cardiovascular health in a new way, paired with his deep understanding of the existing landscape, was attractive: “What I liked about Jeff was that he was from that world, but he was not of that world,” said Maqubela.
He added that Kindred is more than willing to invest in founders before they have a product or even a prototype, but that there is certain criteria involved. Alongside domain insight, Kindred also looks for personality that people want to partner with. As part of the firm’s investment due diligence in Wessler, Kindred helped recruit technical co-founding partners.
“The theory was that if one of them was ready to quit their ‘insert great job X’ to go work with this cardiologist, that’s actually a really important input that he is CEO material as well as a clinician,” said Maqubela.
TAM
As we dove into the pitch deck, Wessler and Maqubela both highlighted an early slide (pictured below).
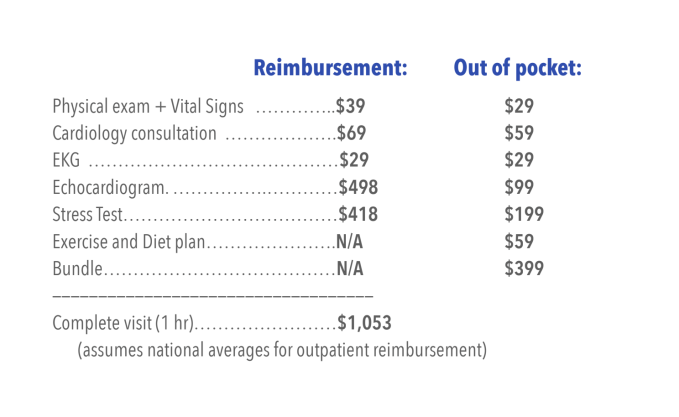
We often hear that heart disease is the number-one killer, but the extra context around the problem of heart disease itself was critical in telling the Heartbeat Health story. The slide described cardiovascular disease as a bigger threat than all cancers combined, but is 80% preventable.
“It’s the biggest health issue facing America and has humongous impact,” said Maqubela. “Everyone I’ve spoken to since day one of Heartbeat Health, either in a pitch capacity or a recruitment capacity or from our team, has experience with heart disease, with friends or family or loved ones in one way or another. It’s a problem that gripped you.”
One of the key factors any good venture investor looks for is the size of the market. When you realize that everyone you’ve spoken with is in some way affected by heart disease, it becomes evident that the market is absolutely massive. Heartbeat Health benefited from the fact that heart disease is both an emotional burden for almost everyone, and also ‘an incredibly valuable business problem to solve.’
At the early stage, TAM is often evaluated alongside business model. Though Heartbeat Health’s model has changed significantly since then — from D2C to B2B2C — it still resonated with Kindred.
Heartbeat Health Pitch Deck by Jordan Crook on Scribd
“When I look at a business model, I’m looking for heuristics — that the things you’re going to be able to do on the basis of the team and your product are going to translate closely enough into large amounts of money,” said Maqubela, as he literally waved his hand in the air.
“Close enough is literally hand-wavy, at this stage, because you just don’t know and you’re going to have to figure it out. What I looked at when I saw this was ‘How many patients a month?’ and ‘How much money per patient?’ and ‘How many people have heart disease?’ and ‘How hard is it going to be to do this?’ … Well, suddenly I’m getting the big numbers.”
The pivot
Venturing away from the deck for a moment, Wessler and Maqubela started to explain the decision to pivot the model from D2C to B2B2C.
Wessler had this to say:
We were building a model around people who wanted to try the new fancy thing, but didn’t really need us at that time, and so we weren’t really making significant changes in their long-term outcomes. So we had a pretty hard decision as a company to take this from a ‘nice-to-have’ to a ‘need-to-have’ for the whole country, and ultimately the world.
If we’re going to do that, then we have to show that Heartbeat can influence these expensive, incredibly dangerous outcomes of heart disease, and that we can reduce the number of heart issues and events that are happening.
To do that, we had to get into the payor world. The payor 101 primer for healthcare is: it’s incredibly hard to break into. In order to do it, you have to invest a lot in proving outcomes and demonstrating that the model, whatever it is, is going to lower the costs of disease state and improve the outcomes with no sacrifice in quality or at a better quality.
And that takes years to show. So we ultimately sat down and decided that this is the way we’re going to get to this long-term vision. We’ve got to invest years in it. It’s not going to happen over six months. And we made the decision to lean hard into that.
Now, Heartbeat Health focuses on helping cardiologists and clinicians acquire customers well before they get sick. Between the pre-seed and the Series A, Maqubela realized that there are entire industries, particularly in digital health, where distribution is not a separate part of the business, but rather the product itself.
He explained that heart health itself isn’t a difficult problem to solve. If you check your blood pressure early, eat and sleep well, stop smoking, and maybe take relevant medicines, you’re probably going to be better off.
“But how do you get those things to people when they need them?” he mused. “How do you get those things to people early enough? Actually, distribution is the rub. Distribution isn’t just a tactic that you use to sell your products. Distribution is the product.”
Understanding that distribution was the core problem to solve shifted the way Heartbeat Health did business. The company decided to build a suite of distribution pathways and optimized those pathways, understanding that those channels are as core to the product offering as anything else.
Build it
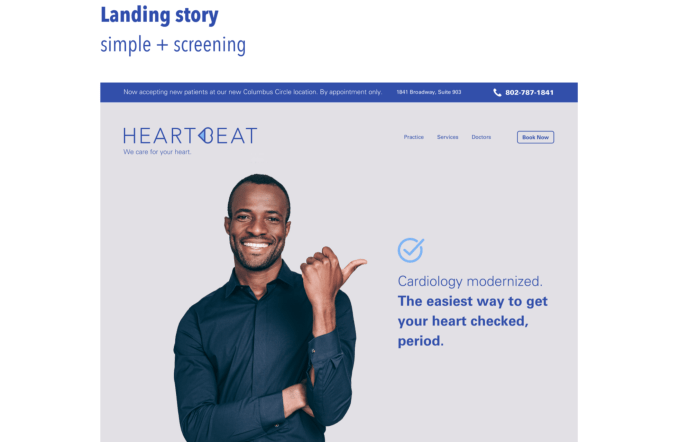
As we returned to the deck, Maqubela highlighted a slide that I would have never expected him to select.
The slide showed a picture of a landing page. But Maqubela said that seeing that landing page, and noting that it had a real phone number on it, told him something critical: you’re able to build a website. At a very basic level, Maqubela is looking for someone who is willing to take the time and energy to learn to build something.
“One of the things at the seed stage that I’m trying to evaluate is… for every person who can create a deck, you divide that by x to find the number of people who can create a deck and also build the things in that deck,” said Maqubela.
But a website is far from the only thing that Wessler was building.
Early on, Heartbeat had decided to have its own physical footprint in the world: a clinic where it would have its own doctors using its own technology and products to serve patients. Wessler said it was the worst early decision and best long-term decision that the team made. Worst because it took up all of the team’s energy and attention, not only because it is resource-consuming to build a practice, but also because of the responsibility that comes with seeing and caring for patients that is separate from the responsibility of building a tech company.
“In the long run, it gave us a real testing ground for patients and clinicians to see what works with patients, what services can and can’t be delivered virtually, and how we go about testing our hypotheses in real time,” said Wessler.
“Now, a couple of years later, I think that practice gave us a huge leg up, because we’re not building in a vacuum. We sell our products to someone else and because of that practice, we’ve already figured out what works and achieved some degree of product-market fit internally. We have data to back up what works and show our successes.”
I asked Maqubela about the decision to build a practice alongside the tech company, and how he evaluates founders that insist on a physical footprint as part of their business.
“The best founders don’t ever conduct an experiment without a very clear point of view for what they’re trying to prove, and how, based on the evidence, what they’re going to do next,” said Maqubela. “If you want to do brick-and-mortar for psychiatric services because ‘insert hypothesis here,’ and if that hypothesis is really interesting and can be proven in some way, then go put down some brick and go put down some mortar.”
You can check out the full conversation with Wessler and Maqubela below, including their feedback to our TechCrunch Live Pitch-off companies.






























Comment