HashiCorp filed go public this week, becoming the latest addition to our growing roster of expected fourth-quarter IPOs.
The cloud infrastructure unicorn presents an interesting mix of open source and proprietary code, with recurring revenues and a nascent hosted product.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on TechCrunch+ or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
To understand HashiCorp’s performance, we’ll need to spend a minute talking about how it approaches the market. If you are a fan of open source software (OSS) or curious how companies with a core of open code make money, it should be an interesting read.
 In very broad terms, HashiCorp grew about 50% in its most recent quarter from a year earlier, but with narrower losses. The company has reached nine-figure revenue scale, meaning that the unicorn worth some $5 billion or so back in 2020 is going to make a splash when it lists.
In very broad terms, HashiCorp grew about 50% in its most recent quarter from a year earlier, but with narrower losses. The company has reached nine-figure revenue scale, meaning that the unicorn worth some $5 billion or so back in 2020 is going to make a splash when it lists.
No more throat clearing, let’s talk OSS, how it shakes out into a business model and how strong HashiCorp’s historical results appear through this July.
HashiCorp’s open source approach
When we wrote above that HashiCorp is a cloud infrastructure company, we meant it. It has built a suite of tools that help other companies manage cloud applications (Terraform), keep them and their data secure (Boundary, Vault), handle networking on a granular level (Consul) and deal with orchestration and cross-platform deployment (Nomad, Waypoint).
That’s an incredibly brief overview, but it should give you an idea of the breadth of the software that HashiCorp has built over the course of its life. We expected a good amount of code, frankly; this is a company going public after all, not some middling Series C startup with hopes of one day growing into a unicorn price.
Here’s where things get fun. Per the company’s S-1 filing, it has “deliberately built [its] products using an open-core software development model.” In practical terms, that means that all HashiCorp software products are “developed as open source projects, with large communities of users, contributors, and partners collaborating on their development.”
The Exchange has written some about how OSS has evolved from exoticism to in-market advantage in recent months. For investors just now picking up on the monetization possibilities that open source software can unlock in-market, HashiCorp’s IPO should be a klaxon that they are behind.
Regardless, how does HashiCorp make money from open source software? The company has built proprietary code atop its open source products that it sells, while also offering support and a hosted version of its products.
The company generates revenue in several buckets. The first and biggest bucket is subscription revenues. The second is professional services — this is generally understood, so we’ll leave it alone.
Inside the subscription segment of HashiCorp are revenues from “licenses of proprietary features, support and maintenance revenue (collectively referred to as Support Revenue in the consolidated statements of operations), and cloud-hosted services.”
Here’s what that revenue collection looks like in results terms:
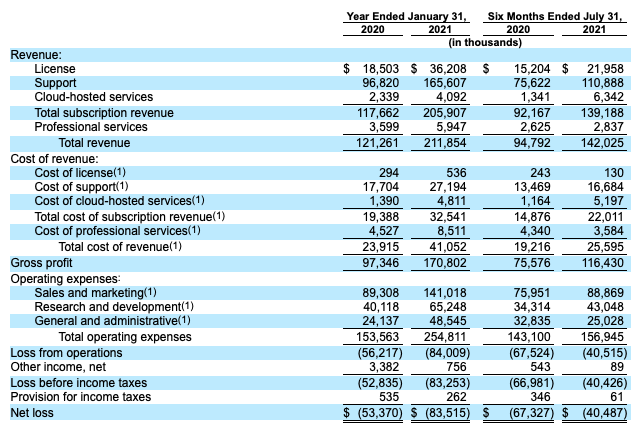
Under the revenue tab, we can see how license, support and cloud-hosted services constitute the subscription line item, which is supplemented by professional services to create a top-line aggregate. From those totals, we can see that HashiCorp grew from $121.3 million in the year ended January 31, 2020 to $211.9 million in the following 12 months, or revenue expansion of just under 75%.
More recently, in the six months ended July 31 or 2020 and 2021, HashiCorp posted revenues of $94.8 million and $142.0 million, respectively. That works out to a more modest growth rate of just under 50%.
Growth at HashiCorp is slowing somewhat rapidly. How the firm can convince public-market investors that it can stem the deceleration will prove critical to how it prices its IPO and is valued when it does debut.
Digging deeper into HashiCorp’s revenues
To better understand each HashiCorp revenue effort, we need to examine them from a gross-margin perspective. Given that the company is calling its largest revenue line item “Support,” you might be worried that it’s a poor revenue category. Let’s find out:
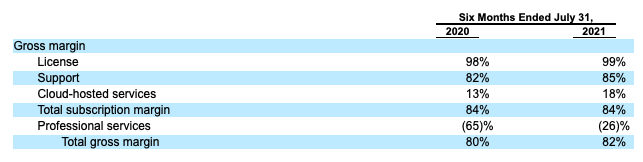
Er, nope. It’s pretty great, frankly, and is only improving. In fact, every piece of the HashiCorp revenue mix posted stronger results over the last two quarters when compared to their year-ago comps.
Notably the company’s hosted solution is putting up the worst gross margins of any revenue item apart from professional services, which are never big generators of gross profit. The hosted product is called “HashiCorp Cloud Platform,” or HCP, which is also the company’s expected ticker symbol, for reference.
HCP is today a small piece of HashiCorp’s business, but the company hopes that it can scale. In its risks section, the unicorn said the following:
Currently, our self-managed offerings represent the majority of our revenues. However, we believe that HCP, our fully managed cloud platform, represents a significant growth opportunity for our business, particularly as an increasing number of our customers are looking for a fully managed offering.
I’d read that as HashiCorp noting that the world is moving toward a more hosted, instead of self-hosted software delivery model. Which, frankly, fits its core product ethos. Today, however, HCP remains modest in terms of its place in the company’s aggregate revenue mix.
The following chart tracks HCP revenues as a portion of total HashiCorp revenues over time:
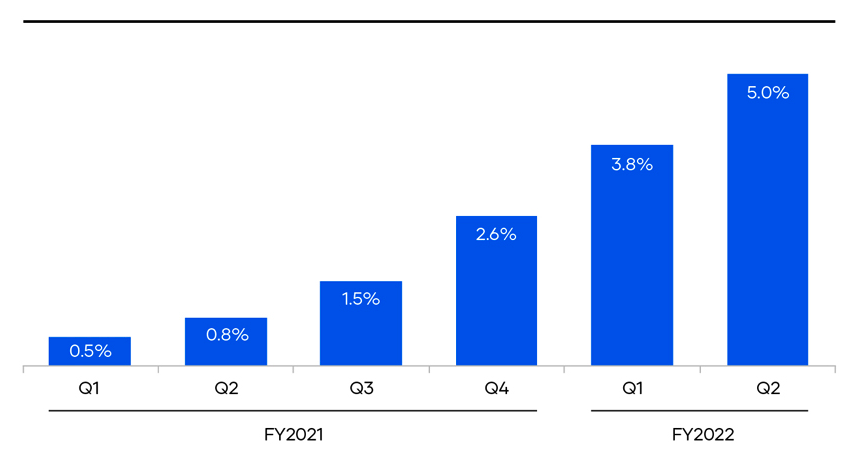
That’s pretty good growth! Recall, however, that HCP has low gross margins at the moment. Perhaps it will see improved profitability as it scales toward a double-digit helping of overall revenues. If not, HashiCorp could wind up seeing its revenue mix shift to a lower gross-margin interval, perhaps at the cost of unlocking future revenue growth.
Given that HashiCorp states that “HCP supplements [its] direct sales motion with a self-serve offering that enables us to serve small- and medium-sized businesses, or SMBs, through a low-touch solution,” it may be that the hosted service will never manage similar gross margins as the other products.
Growth from another perspective
Offering OSS means that HashiCorp’s sales motion is a little different from some enterprise software companies. Instead of landing a customer and then expanding its contract size with its business, HashiCorp pursues what it calls an “adopt, land, expand, and extend” approach to sales.
In practice, HashiCorp looks to see who is using its OSS products or HCP. Then, its “enterprise sales teams land these customers with subscription contracts for our software.” From there, traditional enterprise upselling ensues.
What matters is that while HashiCorp has an extra step in its customer-securing-and-upselling motion than non-OSS companies, it is still posting net retention numbers that impress; being an OSS company is no drag, in other words. Here’s the data:
As of January 31, 2020, January 31, 2021, July 31, 2020, and July 31, 2021, our last four quarter average net dollar retention rate was 131%, 123%, 128%, and 124%, respectively.
No one is going to be stoked that those numbers are slowly drifting lower, but they are all above the 120% mark, so it’s hard to get too cross with HashiCorp. These are good results.
Profitability, etc.
HashiCorp lost more money in each of the full fiscal years — the periods ended January 31, 2019, 2020 and 2021 — posting net losses of $47.4 million, $53.4 million and $83.5 million, respectively.
So, another enterprise software company that is torching cash? Not precisely. In the six months ended July 31, 2021, HashiCorp posted net losses of $40.5 million, down from its year-ago net loss of $67.5 million. It’s good to see the company not only lower its net losses as a percentage of revenue but also cut the number itself.
How did it manage the reduction in net losses? By growing its revenues and resulting gross profit more quickly than it did operating costs. This brought the credit and debits at the firm more closely into sync. HashiCorp remains pretty far from profitability, mind, but at least it can tell investors that the days of rising losses are behind it, provided it can keep up the trend.
If you are in the mood to provide HashiCorp with a chance to make its case concerning adjusted profitability, here you go:
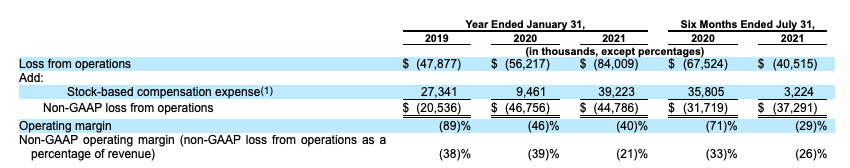
All we are doing here is adding back the cost of share-based compensation to the company’s operating losses, providing a slimmer set of losses. From this perspective, things are somewhat less cheery. After stripping out non-cash, stock compensation costs, HashiCorp actually lost more money in the last two quarters than it did a year earlier, albeit at a lower percentage of revenue.
What’s it worth?
A lot. We know that because HashiCorp generates mostly recurring, high-margin revenues that have proven sticky over time. Investors love that shit.
In its July 31, 2021 quarter, HashiCorp posted revenues of $75.1 million, putting it on an annual run rate of $300.4 million. Given that the company only has to clear the $5 billion valuation mark to best its final private price, we can safely say that it’s in little danger of running afoul of its final, preceding valuation mark.
But what about $10 billion. That’s the number that HashiCorp is rumored to be targeting in its IPO. At that price tag, the company’s run-rate multiple would stretch to to just under 33x. Is that possible? For a company growing at its current pace, yes. But it will be curious to see how HashiCorp’s revenue deceleration plays with its final per-share price and resulting valuation.
More when we get a first price range.






























Comment