Ax Sharma
If combating attacks and hijackings of legitimate software on open source registries like npm weren’t challenging enough, app makers are increasingly experiencing the consequences of software self-sabotage. A developer can, on a whim, change their mind and do whatever they want with their open source code that, most of the time anyway, comes “as is” without any warranty. Or, as seen by a growing trend this year, developers deliberately sabotaging their own software libraries as a means of protest — turning software into “protestware.”
In July, the developer of the widely used atomicwrites Python library Markus Unterwaditzer temporarily deleted his code from the popular code registry PyPI after the site said it would would mandate two-factor authentication for maintainers of “critical projects” — projects that fell into the top 1% of all downloads on the registry. Unterwaditzer’s atomicwrites project matched the criteria and his account was required to be enrolled in two-factor authentication, something he described in a post as “an annoying and entitled move in order to guarantee SOC2 compliance for a handful of companies (at the expense of my free time)” that rely on his code.
Some compared this to the 2016 left-pad incident that briefly broke a large part of the internet after the project’s developer deleted his widely-used code in protest. Developer Azer Koçulu ran into a trademark dispute with messaging app Kik because his npm package was called “kik.” After npm sided with Kik in the dispute, Koçulu withdrew all of his code — 273 modules in all, including the massively popular left-pad library — from the npm registry. It was entirely within his power to do, but it instantly created problems. At the time, the massively popular left-pad package had raked in more than 15 million downloads, and even today the library continues to be downloaded millions of times weekly. As such, in March 2016, developers across the world were left confused — and appalled — when their projects broke because the left-pad component their applications relied on could no longer be found.
What may have seemed like an isolated protest years ago was revived in 2022 by developers sabotaging their own libraries — sometimes to speak out against big corporations, but more recently to protest Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
The recent rise of protestware
A week into 2022, thousands of applications that rely on the heavily used npm projects colors and faker broke and began printing gibberish text on users’ screens. It wasn’t a malicious actor hijacking and altering these legitimate libraries. It turned out the projects’ developer Marak Squires had intentionally corrupted his own work to send a message of protest to big corporations.
Squires’ protest was prompted by the Log4Shell security flaw that burdened Log4j project maintainers, mostly open source volunteers, with patching the critical vulnerability over the December holidays. Squires had earlier expressed frustration at Fortune 500 companies using his open source code for free without offering financial support or sponsoring their upkeep. The Log4Shell vulnerability only reinforced that sentiment — that the businesses ubiquitously reliant on Log4j in their applications have not done enough to support the unpaid volunteers who sustain these critical projects in their free time.
While Squires’ protest only briefly froze projects that rely on the colors library, an entire trend of protestware followed months later with developers sabotaging their own projects, which they had dedicated hundreds of hours to, to object to Russia’s war in Ukraine.
In March 2022, weeks after Russian troops crossed into Ukrainian territory, the popular npm project node-ipc — downloaded over a million times each week — began wiping the machines of suspected Russian and Belarusian developers. The project’s developer, Brandon Nozaki Miller, allegedly sabotaged the code to corrupt the computers it was installed on. Needless to say, the sabotaged versions of node-ipc — now effectively malware — were taken down from the npm registry.
Since then, the protestware theme has evolved into developers indulging in more peaceful protest. Newer versions of open source projects like event-source-polyfill, es5-ext and styled-components simply display a message urging Russia-based users to take action against the war. As such, these versions remain on npm as they do not violate the registry’s policies.
Publishing protestware may not be an easy decision for the developer, either. It puts extra scrutiny on any, and all, versions of the sabotaged project and it can hurt the community’s trust in the developer. Can any software they author, past or future, ever be trusted again?
Evan Jacobs, one of the primary maintainers behind styled-components, told TechCrunch that his project has a history of activism, “most notably our support of the [Black Lives Matter] movement and recommendation to our users to consider donations to the Equal Justice Initiative.” He added: “I had heard that the Russian government was beginning to censor Western news websites and realized that we had a unique opportunity to deliver a concise, informative message via an atypical channel: our npm package installations.”
Jacobs felt it was crucial that Russians get accurate news about the war that is free from state interference. He modified styled-components, which had more than 15 million monthly downloads as of April, to display a bilingual message to Russia-based users summarizing the “many atrocities being committed by the Russian army in Ukraine.”
“Did it make an impact? We’ll probably never know,” Jacobs said. “That being said, I think it was completely worth the chance to disseminate information and hopefully catch the eye of software folks in Russia that might not have seen what was happening otherwise.”
Another developer, Mariusz Nowak, the creator of the es5-ext project, modified later versions of the library to direct Russia and Belarus-based users to accurate news sources like the BBC’s Tor service. Nowak told TechCrunch about the decision to modify the code, saying it was because Russians “are not exactly sure what’s going on, and they’re under influence of their propaganda media,” referring to the strict state control over Russian media. “This message shows only if you install software in Russia, it’s not really visible for other parts of the world,” Nowak said.
Nowak said using his open source library for activism did not affect his credibility among the wider community, but he did receive a handful of angry responses at the beginning.
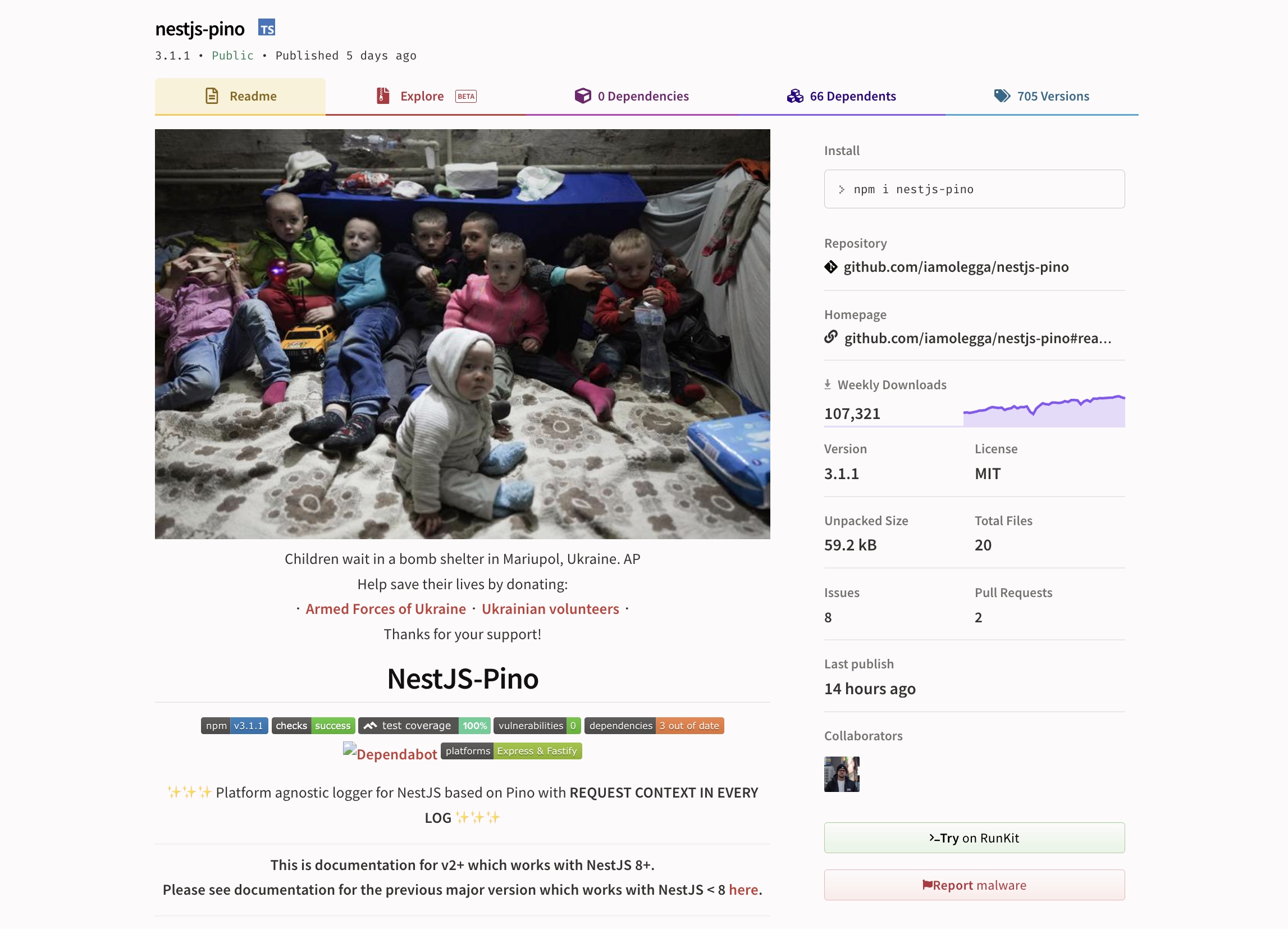
Jacobs and Nowak aren’t alone in retooling their open source code to protest the war. Software supply chain security startup Socket told TechCrunch that nestjs-pino, a popular npm project with over 100,000 weekly downloads, updated its main “readme” file to steer attention to the ongoing crisis in Ukraine. An install script bundled with the package also prints out a console message as soon as it installs.
“You can’t trust what you can’t verify”
Open source developers are discovering new and creative avenues that no longer limit them to implementing new features for their projects, but to actively express their views on larger social matters by modifying their projects for a cause. And, unlike proprietary code that has to function in line with a paying customer’s expectations, most open source licenses are quite permissive — both for the consumer and the developer — offering their code with licenses that offer no guarantees as to what a developer is not supposed to and will never do with their code, making protestware a gray area for defenders.
In fact, as a security researcher at Sonatype, I observed how protestware posed a challenge for us in the early stages and how we would tweak our automated malware detection algorithms to now catch self-sabotages with projects like colors and faker. Traditionally, the system was designed to spot typosquatting malware uploaded to open source repositories, but cases like malicious hijacks or developers modifying their own libraries without warning required a deeper understanding of the intricacies of how protestware works.
The theme has also put major open source registries like npm — owned by GitHub, a Microsoft subsidiary — at a crossroads when having to deal with these edge cases.
Socket’s founder Feross Aboukhadijeh told TechCrunch that registries like GitHub are in a difficult position. “On the one hand, they want to support maintainers’ right to freedom of expression and the ability to use their platform to support the causes they believe in. But on the other hand, GitHub has a responsibility to npm users to ensure that malicious code isn’t served from npm servers. It’s sometimes a difficult balancing act,” said Aboukhadijeh.
A simple solution to ensuring you are getting only vetted versions of a component in your build is to pin your npm dependency versions. That way, even if future versions of a project are sabotaged or hijacked, your build continues to use the “pinned” version as opposed to fetching the latest, tainted one. But this may not always be an effective strategy for all ecosystems, like PyPI, where existing versions of a component can be republished — as we saw in the case of the hijacking of the ctx PyPI project.
“The conversation around ‘protestware’ is really a conversation about software supply chain security. You can’t trust what you can’t verify,” Dan Lorenc, the co-founder and chief executive at Chainguard, a startup that specializes in software supply chain security, told TechCrunch.
Lorenc’s advice against preventing protestware is to follow good open source security hygiene and best practices that can help developers develop protestware more easily and early on. “Knowing and understanding your dependencies, conducting regular scans and audits of open source code you are using in your environments are a start.”
But Lorenc warns the debate about protestware could draw in copycats who would contribute to the problem and detract open source software defenders from focusing on tackling what’s truly important — keeping malicious actors at bay. And with protestware there remain unknown unknowns. What issue is too small — or too big — for protestware?
While no one can practically dictate what an open source developer can do with their code — it is a power developers have always possessed, but are now just beginning to harness.
Updated to correct Squires’ name.






























Comment