Jeff Bussgang
When I was at Open Market in the 1990s, our CEO gave out the recently published book “Crossing the Chasm” to the executive team and told us to read it to gain insight into why we had hit a speed bump in our scaling. We had gone from zero to $60 million in revenue in four years, went public at a billion-dollar market cap, and then stalled.
We found ourselves stuck in what author Geoffrey Moore called “the chasm,” a difficult transition from visionary early adopters who are willing to put up with an incomplete product and mainstream customers who demand a more complete product. This framework for marketing technology products has been one of the canonical foundational concepts to product-market fit for the three decades since it was first published in 1991.
I have been reflecting on why it is that we venture capitalists and founders keep making the same mistake over and over again — a mistake that has become even more glaring in recent years. Despite our exuberant optimism, we keep getting the potential market size wrong. Market sizes have proven to be much, much larger than any of us had ever dreamed. The reason? Today, everyone aspires to be an early adopter. Peter Drucker’s mantra — innovate or die — has finally come to pass.
A glaring example in our investment portfolio is database software company MongoDB. Looking back at our Series A investment memo for this disruptive open-source, NoSQL database startup, I was struck that we boldly predicted the company had the opportunity to disrupt a subsegment of the industry and successfully take a piece of a market that could grow as large as $8 billion in annual revenue in future years.
Have you worked with a talented individual or agency who helped you find and keep more users?
Respond to our survey and help us find the best startup growth marketers!
Today, we realize that the company’s product appeals to the vast majority of the market, one that is forecast to be $68 billion in 2020 and approximately $106 billion in 2024. The company is projected to hit a $1 billion revenue run rate next year and, with that expanded market, likely has continued room to grow for many years to come.
Another example is Veeva, a vertical software company initially focused on the pharmaceutical industry. When we met the company for their Series A round, they showed us the classic hockey stick slide, claiming they would reach $50 million in revenue in five years.
We got over our concerns about market size when we and the founders concluded they could at least achieve a few hundred million in revenue on the backs of pharma and then expand to other vertical industries from there. Boy, were we wrong! The company filed their S-1 after that fifth year showing $130 million in revenue, and today the company is projected to hit $2 billion in revenue run rate next year, all while still remaining focused on just the pharma industry.
Veeva was a pioneer in “vertical SaaS” — software platforms that serve niche industries — which in recent years has become a popular category. Another vertical SaaS example is Squire, a company my partner Jesse Middleton angel invested in as part of a pre-seed round before he joined Flybridge.
When Jesse told me about them — a software company dedicated to barber shops — I thought, “Nice. Sounds like a nice niche opportunity to get to $10+ million and then sell for a good profit.” When they graduated from startup accelerator Y Combinator a number of years ago, they were barely able to scrape together a $1 million seed financing.
“Total available market size was the Achilles heel of our business in the eyes of investors,” co-founder and CEO Songe LaRon shared with me. Those prospective investors who passed ended up being dead wrong. Today, the company is doing hundreds of millions of dollars in transaction volume. A few months ago, Squire announced a $45 million financing at a valuation of $250 million.
I can’t resist one more example. Here are the annual revenue growth rates over the last three years for the largest tech companies in the world:
Amazon: 30%.
Facebook: 29%.
Google: 18%.
These companies are supposed to be mature businesses with hundreds of billions of dollars in revenue, and they are still growing at CAGRs of 20%-30% per year!
Why is it that in recent years, wild-eyed optimistic VCs and entrepreneurs keep undershooting market size across the tech and innovation sector? Upon reflection, I think there are two problems: The chasm is outdated, and Marc Andreessen was right about software eating the world.
Market size definitions: TAM and SAM
To understand our persistent problem with market-size forecasting, let’s first deconstruct total available market (TAM) size. A company’s TAM is a simple formula of the number of potential customers multiplied by the total revenue per customer. TAM is a snapshot of the total dollar potential in the entire market.
Serviceable addressable market (SAM) is the portion of the market that is an actual fit for your product or service. For example, the total global database market is $150 billion. That’s the TAM. But the SAM for MongoDB is the portion of the database market that is a fit for their particular approach, NoSQL. That is projected to be $22 billion in a few years. That’s the SAM.
Typically, we are trained to think that only a portion of the SAM is obtainable within any reasonable window of time because of the chasm.
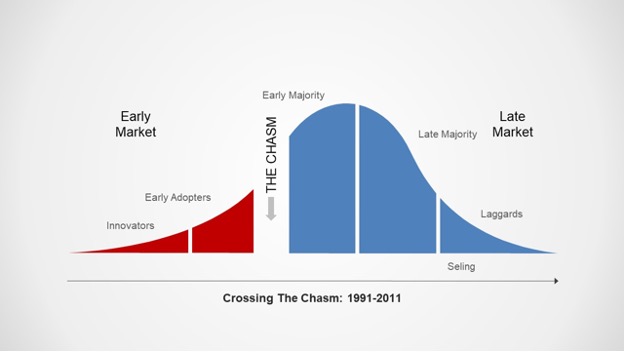
The chasm: 1991-2011
In characterizing why it was so hard for technology companies to introduce discontinuous innovations, Moore framed a technology lifecycle that described different types of customers.
“Our attitude toward technology adoption becomes significant any time we are introduced to products that require us to change our current mode of behavior or to modify other products and services that we rely on,” he observed.
He divided up the different customer groups based on their psychographic profile and attitude toward technology adoption into a bell curve: innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority and laggards. In between the early adopters and the early majority is a chasm.
The chasm, Moore explains, is due to the fact that early adopters are open to change; they aspire to “get a jump on the competition … and expect a radical discontinuing between the old ways and the new.” In contrast, the early majority is “looking to minimize the discontinuity with the old ways. They want evolution, not revolution.”
The image below from Moore’s book lays out the early market versus late market contrast and all of the subdivisions nicely.
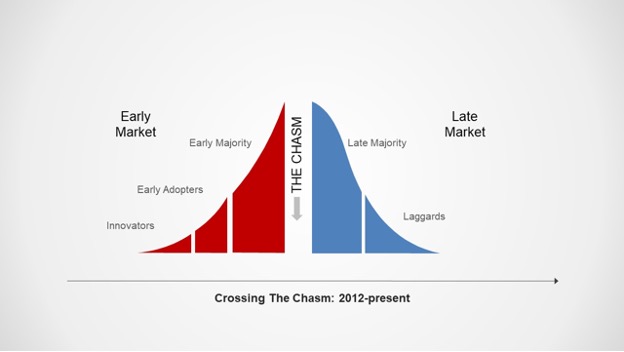
The chasm: 2012-present
In recent years, this model for technology has broken down. The reason, I submit, ties to Marc Andreessen’s famous Wall Street Journal column, “Why Software Is Eating the World.”
Andreessen correctly voiced what many of us in the industry felt when he wrote, “We are in the middle of a dramatic and broad technological and economic shift in which software companies are poised to take over large swathes of the economy.”
Over the last 10 years since that piece was written, businesses finally get it. And this year, in particular, the pandemic helped accelerate a global appreciation that digital innovation was no longer a luxury but a necessity. As such, companies could no longer wait around for new innovations to cross the chasm. Instead, everyone had to embrace change or be exposed to an existential competitive disadvantage.
Using Moore’s framework and combining it with Andreessen’s observation, I would argue that the early market overall (which includes innovators, early adopters and the early majority) has grown substantially larger than before and, further, that due to competitive necessity, the early majority has embraced change and jumped across the chasm. And the portion of the market that the late majority and laggards represent is smaller than ever before.
This corporate imperative to embrace change, which extends to consumers who are more comfortable adopting technology products than ever before, coupled with the fact that software has become a more and more valuable portion of the world, is what is driving surprisingly massive market sizes.
Dramatic market expansion
Looping back to our market size definitions, “software eating the world” has dramatically expanded the TAM while also catalyzing a compressed technology adoption lifecycle, which has dramatically expanded the SAM.
This trend toward rapidly growing and ever-expanding market sizes, and their signal as a leading indicator toward value creation, represents a promising development in our innovation ecosystem. Faster adoption cycles have a positive feedback loop on innovation: The more companies and consumers adopt new technologies, the more entrepreneurs can get funded to build the next new thing.
Even startups on tight budgets can maximize their marketing impact































Comment