Stability AI, the venture-backed startup behind the text-to-image AI system Stable Diffusion, is funding a wide-ranging effort to apply AI to the frontiers of biotech. Called OpenBioML, the endeavor’s first projects will focus on machine learning-based approaches to DNA sequencing, protein folding and computational biochemistry.
The company’s founders describe OpenBioML as an “open research laboratory” — and aims to explore the intersection of AI and biology in a setting where students, professionals and researchers can participate and collaborate, according to Stability AI CEO Emad Mostaque.
“OpenBioML is one of the independent research communities that Stability supports,” Mostaque told TechCrunch in an email interview. “Stability looks to develop and democratize AI, and through OpenBioML, we see an opportunity to advance the state of the art in sciences, health and medicine.”
Given the controversy surrounding Stable Diffusion — Stability AI’s AI system that generates art from text descriptions, similar to OpenAI’s DALL-E 2 — one might be understandably wary of Stability AI’s first venture into healthcare. The startup has taken a laissez-faire approach to governance, allowing developers to use the system however they wish, including for celebrity deepfakes and pornography.
Stability AI’s ethically questionable decisions to date aside, machine learning in medicine is a minefield. While the tech has been successfully applied to diagnose conditions like skin and eye diseases, among others, research has shown that algorithms can develop biases leading to worse care for some patients. An April 2021 study, for example, found that statistical models used to predict suicide risk in mental health patients performed well for white and Asian patients but poorly for Black patients.
OpenBioML is starting with safer territory, wisely. Its first projects are:
- BioLM, which seeks to apply natural language processing (NLP) techniques to the fields of computational biology and chemistry
- DNA-Diffusion, which aims to develop AI that can generate DNA sequences from text prompts
- LibreFold, which looks to increase access to AI protein structure prediction systems similar to DeepMind’s AlphaFold 2
Each project is led by independent researchers, but Stability AI is providing support in the form of access to its AWS-hosted cluster of over 5,000 Nvidia A100 GPUs to train the AI systems. According to Niccolò Zanichelli, a computer science undergraduate at the University of Parma and one of the lead researchers at OpenBioML, this will be enough processing power and storage to eventually train up to 10 different AlphaFold 2-like systems in parallel.
“A lot of computational biology research already leads to open-source releases. However, much of it happens at the level of a single lab and is therefore usually constrained by insufficient computational resources,” Zanichelli told TechCrunch via email. “We want to change this by encouraging large-scale collaborations and, thanks to the support of Stability AI, back those collaborations with resources that only the largest industrial laboratories have access to.”
Generating DNA sequences
Of OpenBioML’s ongoing projects, DNA-Diffusion — led by pathology professor Luca Pinello’s lab at the Massachusetts General Hospital & Harvard Medical School — is perhaps the most ambitious. The goal is to use generative AI systems to learn and apply the rules of “regulatory” sequences of DNA, or segments of nucleic acid molecules that influence the expression of specific genes within an organism. Many diseases and disorders are the result of misregulated genes, but science has yet to discover a reliable process for identifying — much less changing — these regulatory sequences.
DNA-Diffusion proposes using a type of AI system known as a diffusion model to generate cell-type-specific regulatory DNA sequences. Diffusion models — which underpin image generators like Stable Diffusion and OpenAI’s DALL-E 2 — create new data (e.g. DNA sequences) by learning how to destroy and recover many existing samples of data. As they’re fed the samples, the models get better at recovering all the data they had previously destroyed to generate new works.

“Diffusion has seen widespread success in multimodal generative models, and it is now starting to be applied to computational biology, for example for the generation of novel protein structures,” Zanichelli said. “With DNA-Diffusion, we’re now exploring its application to genomic sequences.”
If all goes according to plan, the DNA-Diffusion project will produce a diffusion model that can generate regulatory DNA sequences from text instructions like “A sequence that will activate a gene to its maximum expression level in cell type X” and “A sequence that activates a gene in liver and heart, but not in brain.” Such a model could also help interpret the components of regulatory sequences, Zanichelli says — improving the scientific community’s understanding of the role of regulatory sequences in different diseases.
It’s worth noting that this is largely theoretical. While preliminary research on applying diffusion to protein folding seems promising, it’s very early days, Zanichelli admits — hence the push to involve the wider AI community.
Predicting protein structures
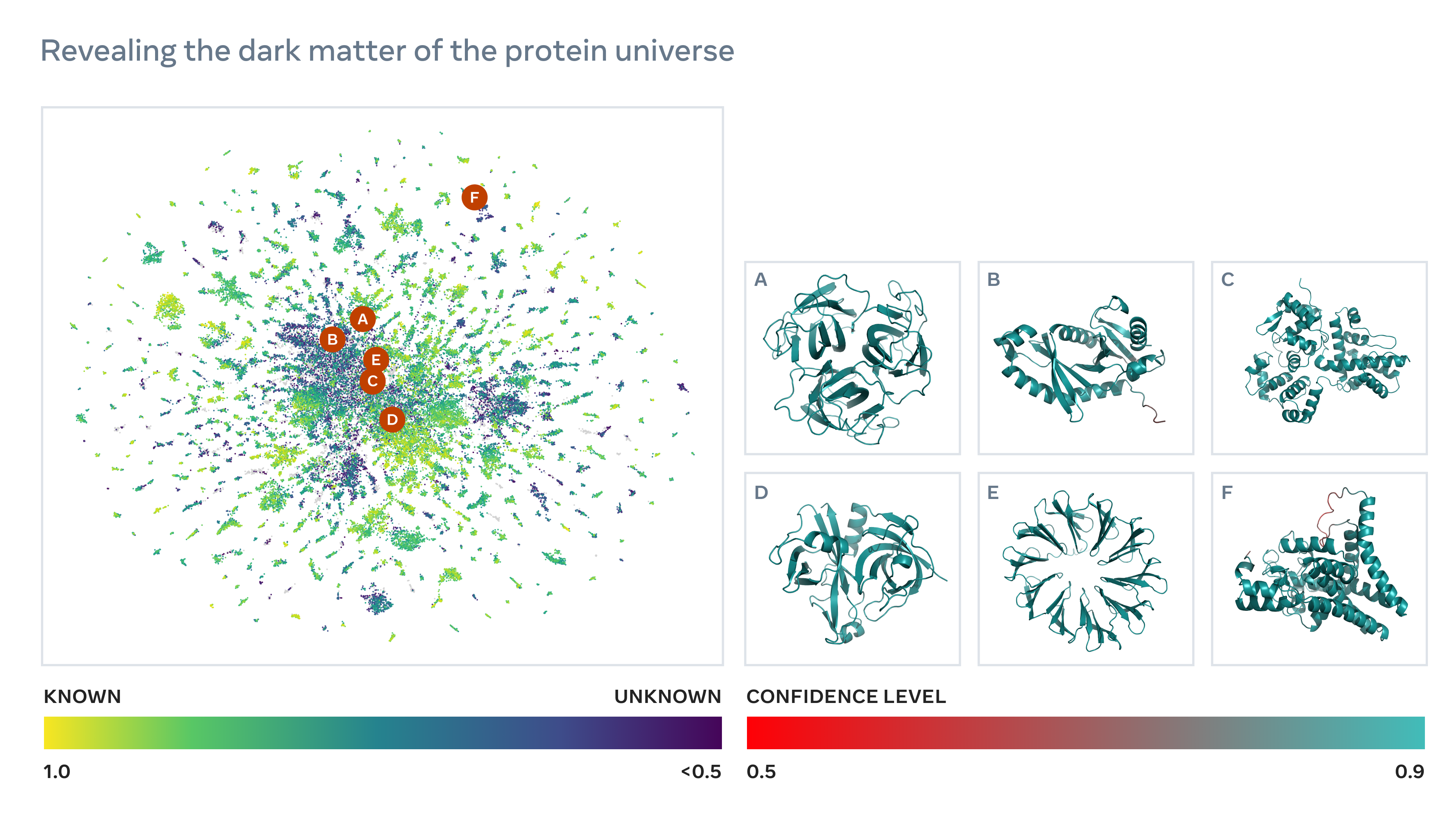
OpenBioML’s LibreFold, while smaller in scope, is more likely to bear immediate fruit. The project seeks to arrive at a better understanding of machine learning systems that predict protein structures in addition to ways to improve them.
As my colleague Devin Coldewey covered in his piece about DeepMind’s work on AlphaFold 2, AI systems that accurately predict protein shape are relatively new on the scene but transformative in terms of their potential. Proteins comprise sequences of amino acids that fold into shapes to accomplish different tasks within living organisms. The process of determining what shape an acids sequence will create was once an arduous, error-prone undertaking. AI systems like AlphaFold 2 changed that; thanks to them, over 98% of protein structures in the human body are known to science today, as well as hundreds of thousands of other structures in organisms like E. coli and yeast.
Few groups have the engineering expertise and resources necessary to develop this kind of AI, though. DeepMind spent days training AlphaFold 2 on tensor processing units (TPUs), Google’s costly AI accelerator hardware. And acid sequence training data sets are often proprietary or released under non-commercial licenses.
“This is a pity, because if you look at what the community has been able to build on top of the AlphaFold 2 checkpoint released by DeepMind, it’s simply incredible,” Zanichelli said, referring to the trained AlphaFold 2 model that DeepMind released last year. “For example, just days after the release, Seoul National University professor Minkyung Baek reported a trick on Twitter that allowed the model to predict quaternary structures — something which few, if anyone, expected the model to be capable of. There are many more examples of this kind, so who knows what the wider scientific community could build if it had the ability to train entirely new AlphaFold-like protein structure prediction methods?”
Building on the work of RoseTTAFold and OpenFold, two ongoing community efforts to replicate AlphaFold 2, LibreFold will facilitate “large-scale” experiments with various protein folding prediction systems. Spearheaded by researchers at University College London, Harvard and Stockholm, LibreFold’s focus will be to gain a better understanding of what the systems can accomplish and why, according to Zanichelli.
“LibreFold is at its heart a project for the community, by the community. The same holds for the release of both model checkpoints and data sets, as it could take just one or two months for us to start releasing the first deliverables or it could take significantly longer,” he said. “That said, my intuition is that the former is more likely.”
Applying NLP to biochemistry
On a longer time horizon is OpenBioML’s BioLM project, which has the vaguer mission of “applying language modeling techniques derived from NLP to biochemical sequences.” In collaboration with EleutherAI, a research group that’s released several open source text-generating models, BioLM hopes to train and publish new “biochemical language models” for a range of tasks, including generating protein sequences.
Zanichelli points to Salesforce’s ProGen as an example of the types of work BioLM might embark on. ProGen treats amino acid sequences like words in a sentence. Trained on a dataset of more than 280 million protein sequences and associated metadata, the model predicts the next set of amino acids from the previous ones, like a language model predicting the end of a sentence from its beginning.
Nvidia earlier this year released a language model, MegaMolBART, that was trained on a dataset of millions of molecules to search for potential drug targets and forecast chemical reactions. Meta also recently trained an NLP called ESM-2 on sequences of proteins, an approach the company claims allowed it to predict sequences for more than 600 million proteins in just two weeks.
Looking ahead
While OpenBioML’s interests are broad (and expanding), Mostaque says that they’re unified by a desire to “maximize the positive potential of machine learning and AI in biology,” following in the tradition of open research in science and medicine.
“We are looking to enable researchers to gain more control over their experimental pipeline for active learning or model validation purposes,” Mostaque continued. “We’re also looking to push the state of the art with increasingly general biotech models, in contrast to the specialized architectures and learning objectives that currently characterize most of computational biology.”
But — as might be expected from a VC-backed startup that recently raised over $100 million — Stability AI doesn’t see OpenBioML as a purely philanthropic effort. Mostaque says that the company is open to exploring commercializing tech from OpenBioML “when it’s advanced enough and safe enough and when the time is right.”





























Comment