Gnawing, burrowing, infecting: The damages caused to agriculture by insect pests like the Japanese beetle (pictured above) exceed $100 billion every year, according to the Agricultural Research Service of the USDA. And along with plant diseases, which the exoskeleton buggers can also transmit, arthropods account for the annual 40% loss of agricultural production worldwide.
Enter FarmSense, a Riverside, California-based agtech startup attempting to solve the insect pest problem. The company creates optical sensors and novel classification systems based on machine learning algorithms to identify and track insects in real time. The key here: real-time information.
They claim real-time information provided by their sensors allows for early detection and thus the timely deployment of pest-management tools, such as insecticide or biocontrols. The current mechanical traps used for monitoring may only yield important intel 10 to 14 days after the bugs’ arrival.
“Some of these bugs only live as adults for like five days, so by the time you know you have a problem, the problem has already taken root and is now a bigger problem,” said Eamonn Keogh, a co-founder of FarmSense. “Had you known about it in real time, you could have localized the intervention to just one location and had a much better outcome, saving pesticide, saving labor and saving the crop from being damaged.”
How they can provide the information critical for achieving those better outcomes is a bit complicated.
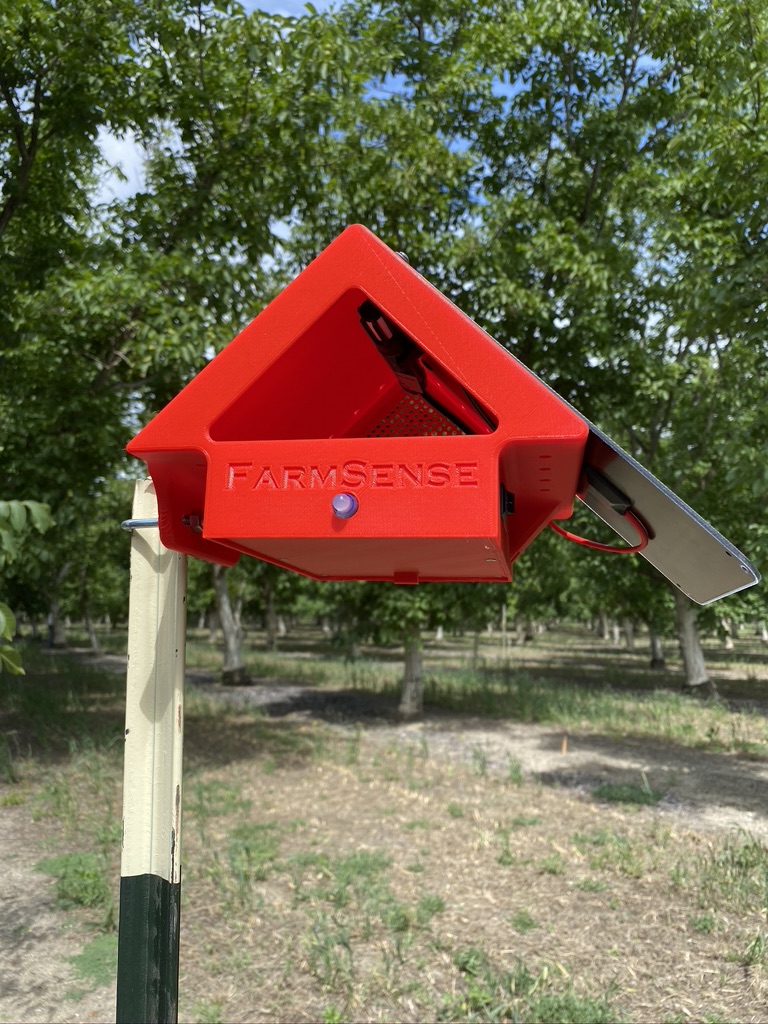

Currently being tested and researched in almond orchards in Southern California thanks to a Small Business Innovation Research grant, their newest sensor, termed the FlightSensor, is best understood when considering where Keogh got the idea for it: James Bond and Cold War espionage.
Keogh explained how Russian spies would use lasers, poised on glass window panes, to pick up on vibrations caused by people’s voices. Then a sensor would translate that information, providing rough intel on what was going on in the room.
“With the same kind of trick in mind, I imagined what would happen if a bug flew past a laser… you would hear just the bug and nothing else.”
However, instead of reading vibrations, the FlightSensor uses light curtains and shadows within a small tunnel that the insects are drawn into by attractants. On one side of the sensor is a light source and on the other the optical sensor. The sensor measures how much light is occluded, or rather how much makes it across, when an insect flies inside. That data is turned into audio and analyzed by machine learning algorithms in the cloud.
According to FarmSense, the sensor, which is designed to look like old analog devices for ease-of-use by growers, does not pick up on ambient noises, such as wind or rainfall.
“The quality of the signal is so beautifully clear and it’s so deaf to the ambient sounds normally heard in the field,” Keogh said. “It’s essentially a different modality to hear the insect, but when you put on headphones and listen to the audio clip from the sensor, it sounds just like a mosquito or a bee flying around.”
Keogh, a professor of computer science and engineering at UC Riverside, specializes in data mining and works on the novel machine learning algorithms that FarmSense employs for identification purposes. Assisting on the development and deployment are entomologists and field specialists, including co-founder Leslie Hickle.
Shailendra Singh — the company’s CEO who has developed systems for wireless and cellular networks as well as security — works on the hardware side. He provided a working price point for each sensor, which will be billed by the season, at $300.
The impact of this technology is clear. For farmers tending to fields large and small, real-time information on insects would not only be important for their financial security, but would also allow them to potentially conserve and protect critical resources, such as soil health.
But FarmSense claims it wants to empower rural farmers who they say are disproportionately impacted by the damages caused by insects.
Yet $300 per sensor per season is stiff, posing a potential risk to adoption and, thus, to the tech’s ability to even solve the issue of insect damage in the first place.
One of the most difficult things for small scale-farmers is managing risk, said Michael Carter, the director of the USDA-funded Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Markets, Risk, and Resilience and distinguished professor of agricultural and resource economics at UC Davis.
“Risk can keep people poor. It disincentives investment in technologies that would raise income on average, because the future is unknown,” Carter said. “People with low wealth obviously don’t have a lot of savings, but they can’t risk the savings to invest in something that might improve their income that also might cause their family to starve.”
However, he was optimistic that technology like the FlightSensor could alleviate investment dread for small-scale farmers, particularly if the tech were paired with insurance to further protect them.

The technology also raises this question: Is real-time identification really the best option for pest management? Speaking to research entomologist Andrew Lieb of the USDA Forest Service, it might not be. He explained that the primary drivers of invasive insects — typically the most destructive to both agriculture and forests — are travel and trade.
He expressed optimism for technology as a way to control insect establishment, but ultimately thinks that the optimal strategy is to attack the problem even earlier. We should address current import and export laws, how products are treated to remove pests and perhaps even pass travel prohibitions.
Despite these concerns, it is beyond doubt that FarmSense’s technology is poised for impact. Even thinking beyond addressing financial insecurity for farmers and threats to our global food chains, it might prove useful in tracking and spreading critical information about disease-vectoring insects, like mosquitoes.
And with the continual disruption caused by COVID-19, it’s difficult to imagine a world that isn’t keenly aware of how biosecurity’s successes — or failures — ripple throughout our myriad systems.
Looking at how non-native insect invasions are expected to increase by 36% by 2050 and how growing population numbers are going to put greater pressure on food production, innovative tech like the FlightSensor that advances our capacity to understand and thoughtfully respond to threats is more than welcome.
As Carter said about all of the possible ways in which agtech still stands to benefit agriculture, “we need to be creative at those margins.”






























Comment