David Rusenko
When President Joe Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) into law on August 16, 2022, we started looking into its implications, particularly with regard to the impact on the future of the climate and the innovations that might shape that future.
As the most important piece of climate legislation in United States history, the IRA represents a fundamental regulatory inflection that may help create a different future. The purpose of this post is to share our understanding of the regulatory ramifications of this monumental bill, especially as they relate to the problems some of the most capable founders in the world are looking to tackle.
Building electrification
The IRA contains several major programs that aim to accelerate building electrification — the replacing of residential fossil fuel machines with electric equivalents. This has the benefit of eliminating combustion emissions, improving comfort, as well as improving indoor air quality, which can have dramatic positive health impacts.
There are three major programs that incentivize building electrification. The first (Sec. 50122) provides a total of $4.5 billion in funding for appliance replacements and is means tested: It provides up to 100% of project costs for those earning less than 80% of area median income (AMI) and 50% of project costs for those earning less than 150% AMI, with annual limits. Eligible appliances include heat pumps, heat pump water heaters, electric or induction stoves, electric or heat pump clothes dryers, upgraded breaker boxes, electrical wiring upgrades, home energy audits, and insulation and sealing.
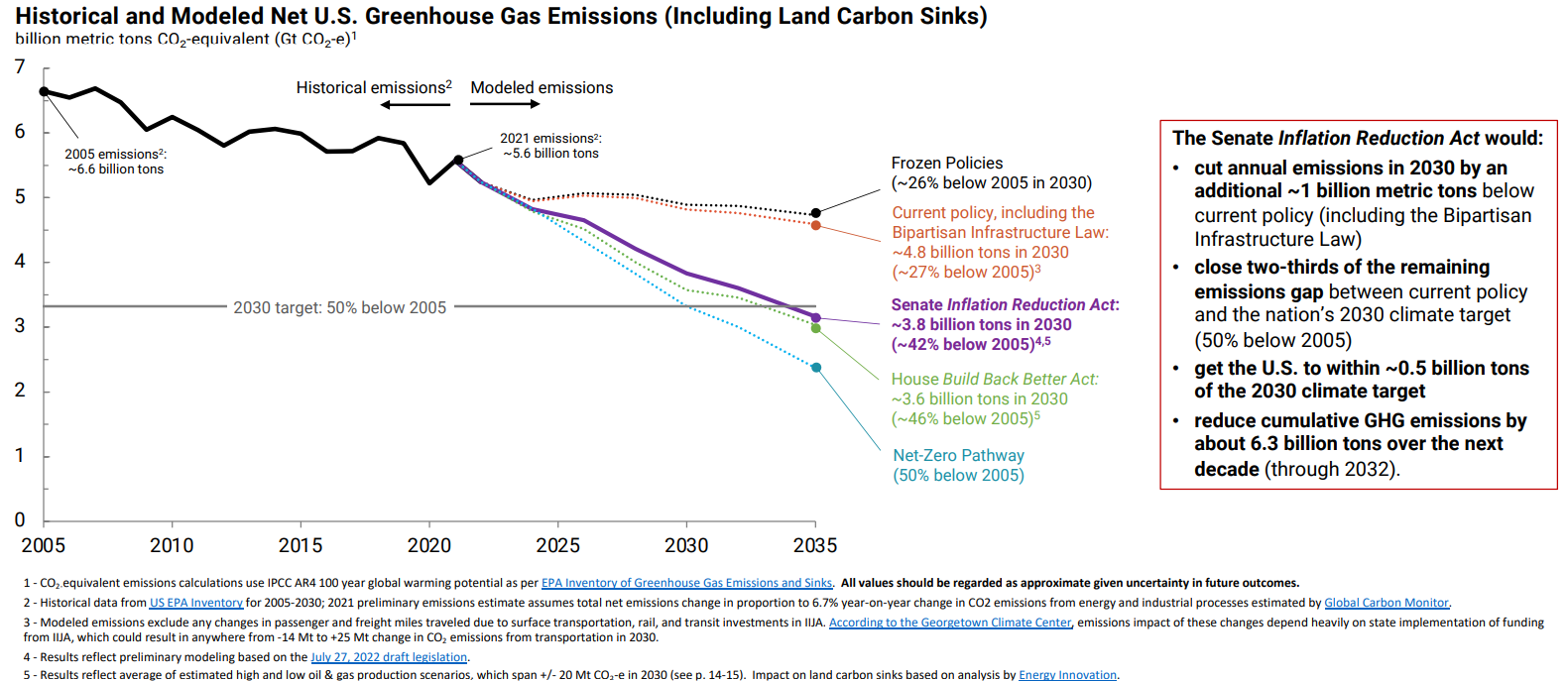
The second program (Sec. 50121) is a performance-based home energy retrofit program that provides up to $4,000 per home, or $8,000 per home for low-to-moderate income households. Projects cannot claim both this program and Sec. 50122.
Both programs can be combined with the third program (Sec. 13302), which expands the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) to a 30% tax credit for eligible projects including residential solar, solar water heating, fuel cell, small wind energy, battery storage and geothermal heat pumps.
The IRA also includes significant and open-ended financing for projects that broadly reduce greenhouse gasses and accelerate deployment of renewable energy, many of which will likely apply to building electrification projects, such as the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund (Sec. 60103), and $40 billion in loan guarantee authority for the Department of Energy (Sec. 50141).
Interesting problems
The funding in the IRA for buildings is likely to catalyze the replacement of fossil fuel machines in buildings and accelerate the adoption of fully electric alternatives. Today, market share of these alternatives is relatively low and contractor adoption and expertise is lacking. Early examples of an increase in consumer demand for these products include Maine and New York.
While we won’t see an overnight shift across the country, these incentives will create a burgeoning market for home electrification, similar to how past laws created a market for residential solar. Problems we have identified include:
- Fragmented contractor market.
- There are not enough trained professionals (electricians, HVAC technicians, etc.).
- Projects tend to be highly custom and time intensive to design and quote.
- Difficult for businesses and consumers to navigate the changing financing/incentives landscape.
- The ROI of these projects will be highly variable and vary from home to home.
- Most home appliances are replaced on failure in an emergency, and most homes are not wired for 220v, so there is a pre-wiring problem to be solved.
- Navigating the retrofit process is time consuming and confusing for consumers, requiring work across multiple contractors that don’t individually plan for holistic project needs (e.g., panel upgrade).
Carbon capture/methane reduction
The latest science tells us that in order to keep warming to 1.5°–2° C, we need to reduce emissions to about 45% lower than 2010 levels by 2030 and achieve net-zero by 2050. It is not realistic to expect that we can replace all of our fossil fuel machines and processes in that time frame.
As such, the IRA includes significant incentives for carbon capture at the point source of emissions in industrial facilities (e.g., natural gas plants). The incentives are much stronger if the carbon is sequestered ($85/ton) than if it is reused ($60/ton). It also includes increased incentives for direct air capture (DAC) at $180/ton (sequestered) or $130/ton (reused).
Methane is estimated to have about 30x greater warming potential than CO2 over a 100-year time frame. However, our largest warming challenges will be in the nearer term, and methane’s 20-year warming potential is about 85x that of CO2. The IRA includes a significant methane fee for petroleum and natural gas facilities, which starts at $900/ton in 2024 and increases to $1,500/ton in 2026. The IRA also includes significant incentives for work that mitigates methane emissions.
Over time, these programs may expand to include more sources of emissions for carbon capture or removal, as well as more industries subject to the methane fee. Founders can judge where the wind is blowing while being careful to understand that not all carbon sequestration projects are made equal — many carbon offset programs today have additionality and permanence concerns.
Interesting problems:
- The science of carbon/methane measurement and data collection needs further development.
- Standardization of protocols will be crucial for system reliability and transparency.
- Transparency of accounting practices will be important for appealing to the demand side of the carbon offsets market.
- As incentives for emissions mitigation are deployed, it will be important to establish equity in this process.
Transportation
Perhaps the most impactful change in our day-to-day lives around climate will be transportation. In total, this bucket accounts for one-fifth of global greenhouse gas emissions, and there are several important elements of the IRA that address this sector.
To dive into the details, Sec. 13401 modifies and extends EV tax credits through 2032. Other considerations for whether something qualifies for the benefit include where the components are made (North America qualifies), how expensive is the car (larger cars below $80,000 and smaller cars below $55,000 qualify) and the income of buyers (AGI less than $300,000 for a joint return and less than $225,000 for head of household). Sec. 13402 provides similar/smaller benefits for used EVs, which will become more important in the coming years.
Similarly, Sec. 13403 addresses commercial clean vehicles, including garbage trucks and school buses, with a similar tax accreditation mechanism. Sec. 13404 also provides subsidies for the construction of fueling stations/charging infrastructure to support the expected increase in electric vehicles. Finally, there is other designated funding to support credits for alternative fuels, some of which more directly impact the transportation sector.
The new EV economy
- The prevalence and expansion of EVs will shift the car manufacturer business model at large. Current OEMs in the United States are bound by dealership laws, but Tesla has shown the power of meeting consumers where they are without spending money on sprawling lots, etc.
- We may see more OEMs follow Volvo’s lead and spin off their EV business units as a mechanism to cleanly separate the businesses. This is not to say that the role of the distributor is dead, but in this new world, the requirements and software for selling these vehicles will be different, thus allowing for new startups to fill in some of these new gaps.
- Opportunities for startups more focused on the end consumer, whether that be EV-specific ancillary businesses or financing mechanisms.
Green fintech
With such a large pool of capital being deployed toward building electrification, agriculture projects, transportation, etc., we believe there will be an opportunity to create financial products and startups that target and support the green sector.
Complexity in new funding and incentive structures will require appropriate mechanisms to manage capital. This concept differs from the “Green Bank” in the IRA , which is a bucket of capital to be invested into clean energy created to help sustain climate-resilient infrastructure and other projects that will be prioritized for underserved communities.
Interesting problems:
- Helping to manage the fragmented and rapidly changing incentives ecosystem (Drata or Vanta for this sector, etc.).
- Purpose-built models for green lending.
- Leveraging Green Bank funds with private-sector capital.
- Productizing offsets in new markets (e.g., home electrification).
- Inventive business models or project finance around vertical specific needs.
Other major programs
The IRA is long (more than 750 pages) and includes 142 individual sections/programs. Other major programs include support for:
- Increased utility-scale renewables production and development, including nuclear.
- Clean hydrogen.
- Sustainable aviation fuel.
- Clean heavy-duty vehicle program (trash trucks, school buses, mail trucks, etc.).
- Agricultural conservation measures.
- Forest and fire management.
- New transmission lines and infrastructure.
- Drought response.
- Eliminating HFCs.
- Support for state and local governments in adopting zero-emissions building codes.
- Support for green manufacturing.
- Zero-emissions ports.
- Highways built with low-carbon materials.
Themes in the IRA
Aside from individual programs, several major themes are weaved throughout the IRA that are likely to cause a shift in labor standards and the prioritization of certain communities or geographies.
Communities of focus
Many programs include significant bonuses for investment in low- and moderate-income households or communities, energy (read: fossil fuel) communities, environmental justice communities and rural communities.
When developing a strategy, it may be worth considering the impact of these incentives and orient initial focus toward those communities with the highest incentives for change.
Labor standards
Many programs reserve the highest incentives for projects that meet prevailing wage and apprenticeship standards. It remains to be seen how these will be defined and implemented in practice, but it does represent a significant shift in the labor market dynamics for private green construction projects. This will likely increase pay significantly and result in higher demand for registered apprenticeship training programs, which could help unlock workforce expansion for in-demand trades (e.g., electricians).
Looking toward Europe
The IRA has instituted meaningful developments toward the governance and financing of influential climate initiatives, but where will it go from here? To gauge long-term regulatory impact, it is worthwhile to look to the EU, which continues to play a leading role in the evolving global climate policy through the UN, the Paris Agreement and as the largest collective funder of climate measures in developing countries.
Specifically, 30% of the NextGenerationEU budget is marked to fight climate change, with the biggest spending categories including energy-efficient buildings, public transport and renewable energy. The “Fit for 55” package strives to legislate the EU’s target of a 55% net reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and reveals the following:
- The EU ETS (emissions trading system) is expanding to impose CO2 costs on building and transportation emissions. This is indicative of the variation in technology/systems/hardware necessary to track emissions across different sectors.
- To improve the LULUCF (land use, land-use change and forestry) sector, the proposal sets a target for at least 310 million tonnes of net CO2 removals by 2030. Success will require enhanced monitoring capabilities and simplification of the rules on accounting and compliance.
- There is a strong focus on renewable and sustainable energy sources. Especially as seen with ReFuelEU Aviation and FuelEU Maritime, which outline increased adoption of green fuels in these sectors.
- By 2035, it will be illegal to sell cars/vans with an internal combustion engine in the EU. As Europe is home to many top auto manufacturers, this will largely impact the automotive market globally and likely drive accelerated electric vehicle adoption.
The Inflation Reduction Act is a fundamental piece of U.S. legislation that will drive impact in the categories discussed above and beyond. Though it is just a starting point, it is a meaningful change event that will serve to inspire and enable the next wave of great innovations (technical, business and otherwise) across not only the areas in the bill and the ones we most distinctly identified — building electrification, carbon capture, electric vehicles and green fintech — but will also have secondary and tertiary benefits in areas that may be harder to envision.
We leave it to you to leverage the power of this meaningful regulatory inflection by developing your own unique insights to unlock the promise of a better and greener future.
Note: Special thanks to Brooke Martin for all her help. Thanks to the Floodgate Team (specifically Ann, Mike, Izzy and Ryland), Philipp Krinner (Arch), Kyle Treige (Pioneer Climate), Hannah Bebbington (Stripe Climate), Jimmy Douglas and Alexander Krey for their thoughts, support and reading through drafts!































Comment