Luca Rossettini
More posts from Luca Rossettini
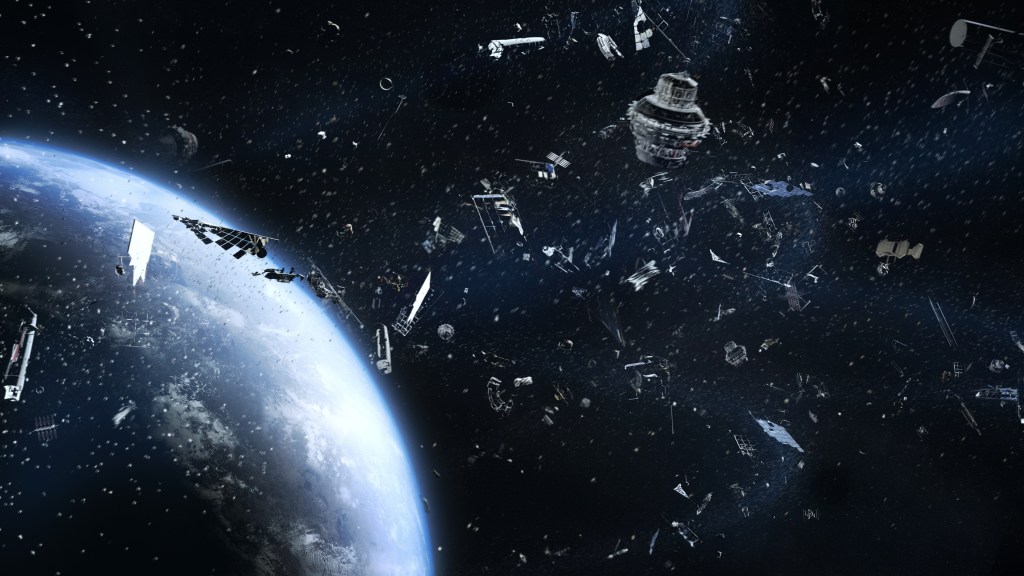
Look up at the sky — hundreds of discarded satellites, spent upper-stage rocket bodies, and mission-related objects circle Earth, posing a risk to space-based services and future missions that will support what is projected to be a trillion-dollar space economy.
According to the European Space Agency, more than 36,500 cataloged objects larger than 10 cm are currently orbiting Earth, along with millions of pieces smaller than 1 cm. Not surprisingly, any collision in orbit can be catastrophic. Traveling at more than 7 km per second — faster than a high-speed bullet — even a 1 cm piece of debris can cause significant damage to a spacecraft and end an entire mission.
Today’s sustainability crisis in space is the result of 60 years of exploration and utilization that have largely ignored the environmental consequences of space activities and treated satellites and other space assets as single-use objects.
The consequence of this approach is an unsustainable model that increases costs and puts the tremendous promise of the space economy at risk. Low-Earth orbits are already so populated that satellite operators are forced to assess conjunctions and perform debris-avoidance maneuvers that consume valuable resources and can disrupt services.
Who’s taking responsibility?
Technical measures alone cannot solve the space sustainability problem. The on-orbit servicing market must be driven by national space policies and international standards that directly support satellite servicing. National regulatory policies are struggling to keep pace with the advancement of technology, the growth of the satellite population, and the development of new activities in orbit.
While multilateral UN provisions, such as the 1967 Outer Space Treaty and the 2019 Guidelines for the Long-term Sustainability of Outer Space Activities, provide high-level guidance, specific licensing practices must be created and implemented by national regulatory agencies in individual countries.
There is no template for the implementation of these guidelines and high-level agreements on an internationally coordinated basis, and global space activity is not under the control of any single national or international entity. Hence, there is no common set of rules that govern global space activity and no mechanisms to ensure the proper disposal of hardware at the completion of space missions. Nor is there any coordinated effort to clean up the decades of space debris already accumulated in orbit.
Attitudes are changing, however, and over the past year, we have seen a significant shift in the urgency around the issue. In June 2021, G7 member nations released a statement confirming orbital debris as one of the biggest challenges facing the space sector and pledged to commit to the safe and sustainable use of space.
While this statement represents a valuable acknowledgment of the scope of our problems with space sustainability, it’s only a step in the right direction. Key players across the international community, from national governments to private commercial companies, must start developing and coordinating space traffic and environmental management.
On-orbit services – the key to a sustainable future
To date, satellite operators haven’t had options for reducing the risks to their satellites in orbit. However, on-orbit servicing is changing this risk scenario. D-Orbit, Astroscale and ClearSpace are joining forces to move the space sector into an era of sustainability, turning on-orbit servicing into an emerging reality.
On-orbit servicing is comparable to roadside car servicing on Earth. Nobody would ever abandon a car in the middle of the highway because the fuel tank is empty or the battery charge runs out. Yet this is exactly how most satellite operators have worked since the dawn of the Space Age, leaving these metaphorical “orbital highways” more congested.
According to applications submitted to the U.S. Federal Communications Commission and International Telecommunications Union, the number of satellites in low Earth orbit is projected to increase by anywhere from 10,000 to 40,000 satellites by 2030, and a single system of over 300,000 satellites has recently been proposed. This growth promises to make a serious issue exponentially worse.
The deployment of a geostationary satellite typically costs $150 million to $500 million. Over the next 15 years, more than 100 geostationary satellites will reach their planned retirement age, driving satellite operators to pursue options for extending the value of their assets, rather than just replacing them. By extending the life of a satellite, servicing enables commercial and institutional operators to be more deliberate in how they use their capital.
Satellite operators — particularly those building larger constellations — can install a low-cost interface on their satellites before launch to reduce the cost and complexity of any future service that might be required. When a satellite fails or reaches the end of its life, a servicer spacecraft can remove it, much like a tow truck assists broken-down cars on a roadway, keeping orbits clear and reducing collision risks to other satellites, including those belonging to the same constellation.
When we extend removal services to on-orbit inspection, operators can assess the condition of their satellites more completely when anomalies arise. With on-orbit relocation services, operators can deliver their satellites from initial deployment to their intended operational orbits, make adjustments to compensate for natural decay, reposition assets within a constellation to address coverage issues, or relocate them to compensate for faults, all without expending their own fuel budget.
As with any other long-term plan requiring significant investments in research and development — like the space race of the 1950s — national governments have an essential role in jump-starting sustainable orbital infrastructure. Active debris removal services are set to emerge, with both the European Space Agency and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency funding debris removal missions in low-Earth orbit in partnership with private entities like ClearSpace and Astroscale.
While solving this global issue requires significant public and private investments, along with systemic changes in the industry, the potential rewards are virtually unlimited. The space economy — a new, unbounded playing field — has the potential to impact life on our planet and open a new frontier across our solar system and beyond.




























Comment