Archita Bhandari
Rachael runs a bakery in New York. She set up shop in 2010 with her personal savings and contributions from family and friends, and the business has grown. But Rachael now needs additional financing to open another store. So how does she finance her expansion plans?
Because of stringent requirements, extensive application processes and long turnaround times, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) like Rachael’s bakery seldom qualify for traditional bank loans. That’s when alternative lenders — who offer short and easy applications, flexible underwriting and quick turnaround times — come to the rescue.
Alternative lending is any lending that occurs outside of a conventional financial institution. These kinds of lenders offer different types of loans such as lines of credit, microloans and equipment financing, and they use technology to process and underwrite applications quickly. However, given their flexible requirements, they usually charge higher interest rates than traditional lenders.
But how do these lenders raise funds to bridge the financing gap for SMBs?
As with all businesses, these firms have two major sources of capital: equity and debt. Alternative lenders typically raise equity funding from venture capital, private equity firms or IPOs, and their debt capital is typically raised from sources such as traditional asset-based bank lending, corporate debt and securitizations.
According to Naren Nayak, SVP and treasurer of Credibly, equity generally constitutes 5% to 25% of capital for alternative lenders, while debt can be between 75% and 95%. “A third source of capital or funding is also available to alternative lenders — whole loan sales — whereby the loans (or merchant cash advance receivables) are sold to institutions on a forward flow basis. This is a “balance-sheet light” funding solution and an efficient way to transfer credit risk for lenders,” he said.
Let’s take a look at each of these options in detail.
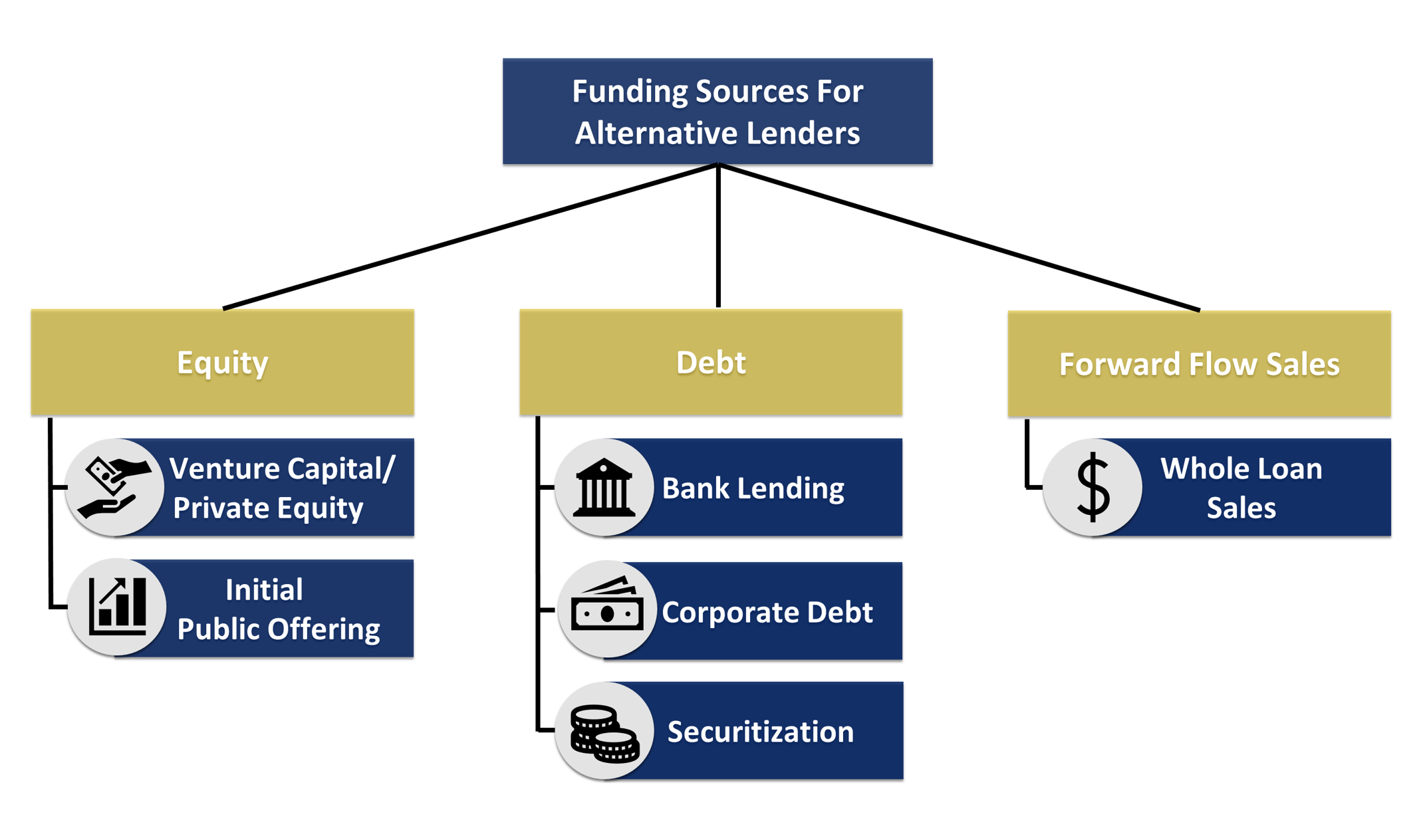
Equity capital
Venture capital or private equity funding is one of the major sources of financing for alternative lenders. The alternative lending industry is said to be a “gold mine” for venture capital investments. While it is difficult for such companies to receive credit from traditional banks because of their stringent requirements in the initial stages, once the founders have shown a commitment by investing their own money, VC and PE firms usually step in.
However, VC and PE firms can be expensive sources of capital — their investment dilutes the ownership and control in the company. Plus, obtaining venture capital is a long, involved and competitive process.
Alternative lenders that have achieved good growth rates and scaled their operations have another option: An IPO lets them quickly raise large amounts of money while providing a lucrative exit for early investors.
Debt capital
Once the business is in good shape, banks can be more willing to lend money through loans and revolving credit facilities. Term loans are the financing provided by traditional banks, credit unions and small business administration (SBA) lenders. Although they offer low interest rates and long payment terms, they require several indicators of security, such as substantial track records and collateral, which nascent alternative lenders do not have.
The other option, the revolving credit facility, is a flexible financing tool that lets the borrower draw down, repay and withdraw funds over and over. These instruments enhance liquidity, as the borrower has ready access to funds to originate new loans as demand increases without any fixed repayment obligations. However, banks perceive alternative lenders as risky businesses because repayment obligations depend not only on the lender’s performance but also on the default risk of the end borrower, which are SMBs for most non-bank lenders.
Securitization is another cost-effective option for raising debt. Lenders can pool the loans they have extended and segregate them into tranches based on credit risk, principal amount and time period. The securities backed by these loans — asset-backed securities (ABS) — can then be sold to investors.
This lets alternative lenders fund more loans by selling securities backed by existing loans and transferring the associated risks to the investors. However, securitization is an overly complex process and does not offer much flexibility to the issuers — alternative lenders, in our case. Unlike bank lending, securitization financings cannot be amended without the approval of a majority of noteholders, who can be hard to track down because these notes are traded in the secondary market.
As the lender grows and has more stable cash flows, it can issue bonds to raise corporate debt from the market. Investors lend money to the issuer in return for interest on the principal, which is paid when the bond matures. Since bonds are a means to raise unsecured debt — not backed by collateral and therefore highly risky for investors — alternative lenders should have a strong balance sheet and reputation in the market to be able to issue them.
The tenure for corporate bonds can be very long compared to bank loans. However, issuing bonds can impose several covenants on the issuer to limit risk and ensure stable financial performance.
Forward flow sales
Established alternative lenders can also raise funds by selling whole loans, which are individual loans issued to borrowers. These loans can be sold on the secondary market to institutional portfolio managers and agencies to transfer their risk and immediately recoup the principal amount.
The deal can be structured in a number of ways to benefit both the lender and the buyer. For example, if a lender is selling a portfolio of its loans, the buyer can pay the servicing fee, a purchase premium and even a back-ended performance payment. The buyer would in turn get the principal and interest payments from the loans.
The illustration below shows the sources of capital used by top SMB non-bank lenders in the U.S. Based on their growth trajectory, most lenders use funding by VC and PE firms as the main source of equity capital, and mostly choose bank loans and securitization for debt financing.
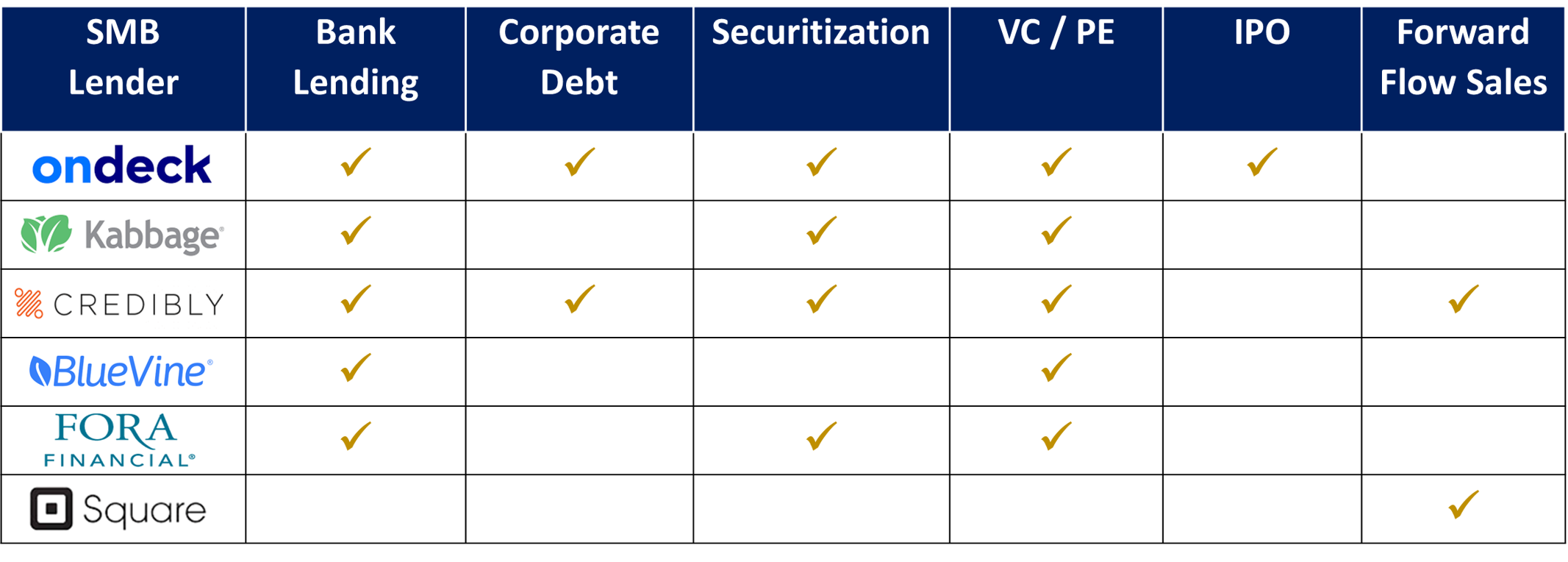
Alternative lenders use the pool of available sources depending on the growth stage of their business. For instance, Kabbage started off with venture capital in 2011 and expanded initially through multiple VC rounds. Then it got a credit line in 2014 and, in 2017, securitized loans to increase originations. It subsequently raised money through a mix of securitization and lines of credit.

But what happens amid dire straits?
Alternative lenders, like most other businesses, have been hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic. Small businesses defaulted on payments and banks stopped origination of new loans, making it difficult for alternative lenders to raise capital to mitigate their liquidity crisis as well as to lend new loans. Most lenders with securitizations faced downgrades of their bond ratings as well.
Could the funding sources utilized by alternative lenders have some role to play in their performance during a crisis?
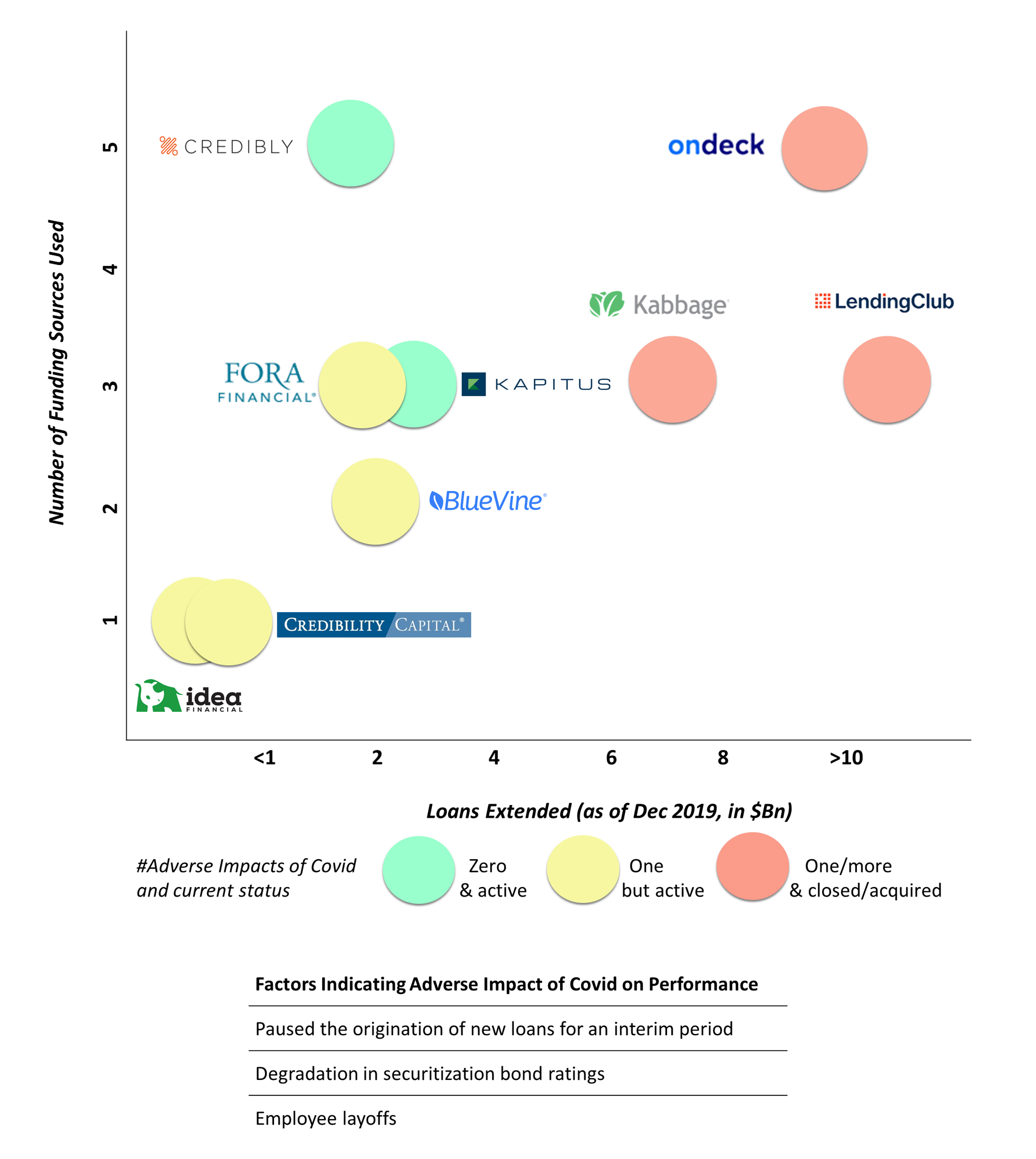
Big lenders like LendingClub, OnDeck and Kabbage suffered the most during COVID-19 and were ultimately acquired or shut down their lending platforms. On the other hand, small lenders like BlueVine and Fora Financial had a rough sail, but they were able to survive and make it to 2021.
Two factors played a role in this: the size of the lender and the number of financing options it had, and restrictive covenants and complexity associated with funding sources like credit facilities and securitization did not offer much-required flexibility.
As loan delinquencies increased during COVID, lenders would have approached banks and investors for additional financing and amendments to existing credit facilities and securitizations. But given the restrictions and risk appetite of banks and the approval from investors involved in getting securitization amendments, big lenders — with more than $15 million of monthly operating expenses — did not get timely access to funds. With no other funding options available, they had to limit their operations as resources dried up.
In this scenario, if the alternative lender goes public, it can raise a large amount of money, but faces a decline in its tolerance to volatility and risk. The illustration below shows what happened with OnDeck and LendingClub — the scattered shareholding resulted in a loss of flexibility, and they were unable to get quick approvals for amendment requests during a time of need.
Smaller lenders, which have less than half the funding requirements as the bigger players, were in a better position to negotiate with banks and ABS investors. For example, Credibly reached out to its noteholders for securitization amendments and was able to continue funding new loans throughout the pandemic.
Kabbage — one of the bigger players — raised $1.2 billion through securitization, which was around 85% of its capital structure during COVID. And in a dire situation, it found it difficult to modify covenants or increase the size of the funding. Though Credibly and Kapitus also had securitizations as the major source of capital, their relative size was small.
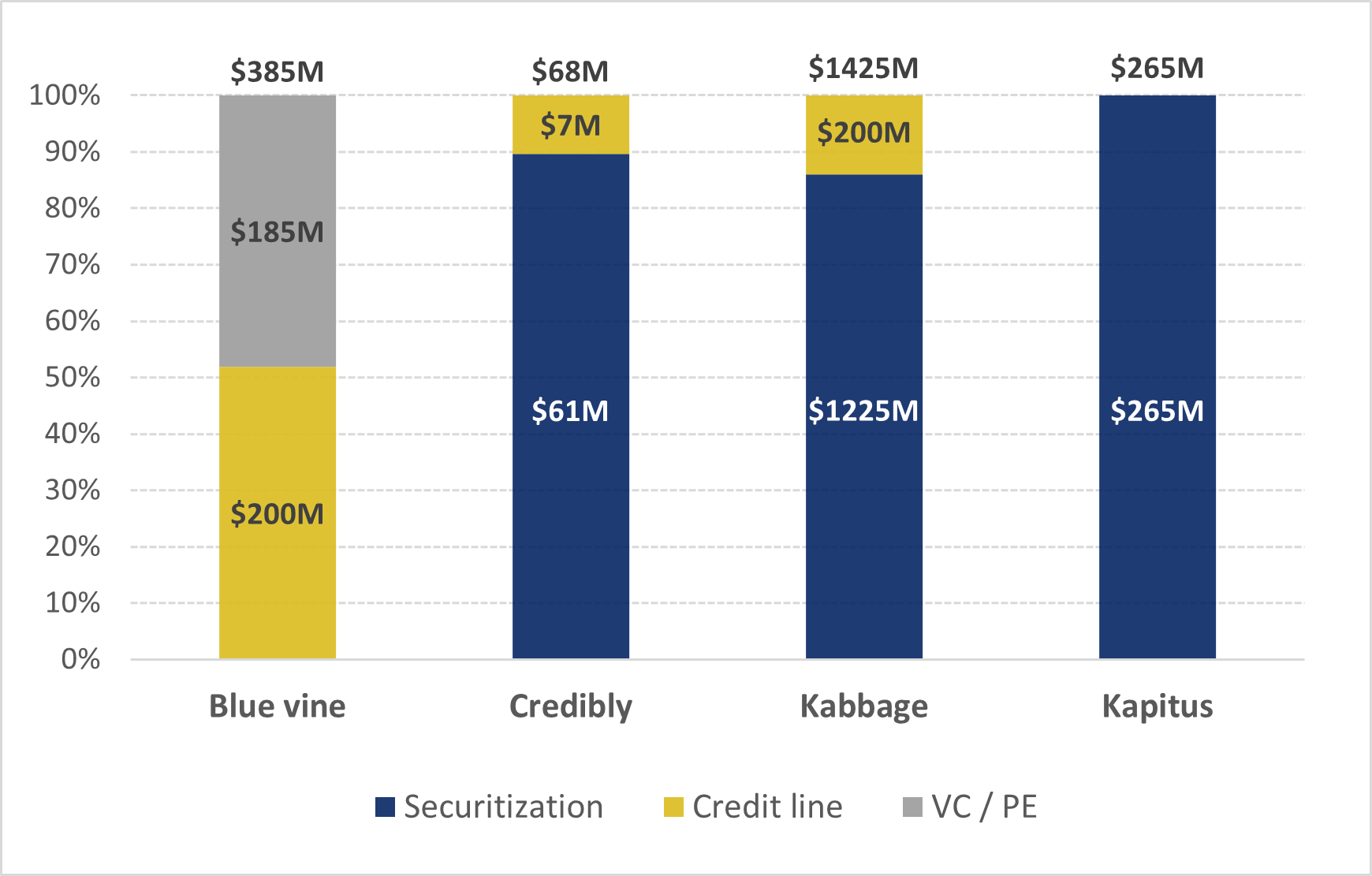
Even if the smaller lenders had to pause origination of new loans, given their size, they could brace themselves until the situation normalized. For example, BlueVine paused lending for a while, but recovered and secured a $75 million revolving credit facility in September 2020.
But for most such alternative lenders, their current sources of capital were not enough to survive the crisis, especially for those with large funding requirements. Only those who were able to find a way through the complexities of their existing capital sources were able to maintain their performance, and the rest were left to perish or find new funding avenues.































Comment