If you haven’t seen Adam McKay’s “Don’t Look Up” starring Meryl Streep, Leonardo DiCaprio and Jennifer Lawrence, you should. The film speaks to an existential, albeit preventative, threat to our world, and well, no one seems to care.
While an allegory, this political piece reflects the climate reality for many. For those who do care, there is no shortage of confusion on how to best tackle this looming threat.
But what if an answer was lying right in front of us? Take that an astounding 40% of global greenhouse gases come from the “Built World.” Forty percent is quite the figure in the context of what’s at stake. In this case, do look up — and to the right, and to the left, because the answer might be all around.
Front and center come the estimated 97 billion square feet of commercial real estate. Despite this sizable footprint and impact on climate, lack of awareness and the real estate industry’s sluggish pace of tech adoption have hampered action until recently.
Adding to this have been misperceptions of returns on investments in climate investments, and frankly, information overload as the industry gets smart about carbon neutrality. Fortunately, evidence is emerging on the ROI of climate tech for both buyers and investors — evidence that could be crucial to usher the “Built World” into an era of carbon neutrality.
Green translates to green
As the saying goes, you have to spend money to make money. And when it comes to reducing real estate’s climate footprint, according to Jones Lang LaSalle (JLL), the path starts with adopting technologies that enable green certifications such as LEED and BREEAM.
Among a host of conclusions, JLL’s report cites that green certifications result in a rent premium of 6% for commercial real estate and a sales premium of 8%. But acknowledgment of climate change and awareness of climate technologies’ efficacy is just the beginning. Knowing where to start brings its own challenges.
To unlock this ROI, property owners have implemented a range of cost saving technologies such as efficient lighting, reimagined cooling and heating systems, and systems to reduce their electricity footprint. After all, to get a LEED certification, buildings must hit a performance score combining metrics across several categories including energy, water, waste, transportation and quality.
To accommodate, technology has popped up transversely across the value chain of designing, constructing and retrofitting parts of the building life cycle to improve metrics across LEED’s target categories. To unpack the opportunity come specific considerations with investments at each point.
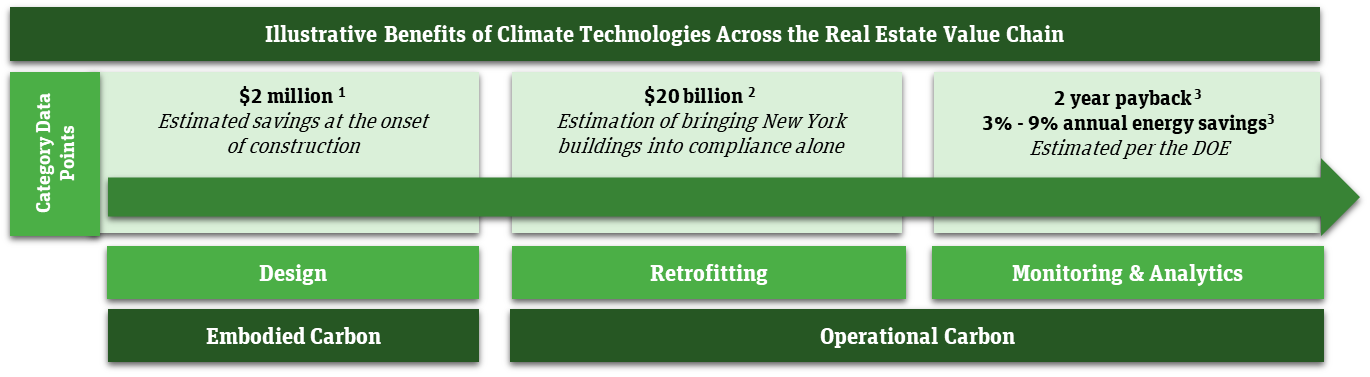
Climate technology solutions across the real estate value chain. 1Estimated per Cove.Tool; 2New York Times “New York’s Real Climate Challenge: Fixing its Aging Buildings”; 3Department of Energy’s “Proving the Busines case for Building Analytics”. Image Credits: SVB Capital.
Design and construction
An ideal, carbon-neutral world might be built from the ground up. Proven technologies such as Cove.Tool and Juno Residential are popping up to enable this brave new world of energy efficiency, starting with just how buildings are designed and what materials they are built from.
While strong proof points exist in this approach, initial data indicates there may be several considerations when evaluating solutions for design and construction. First are early indications of disparity in the expected efficiency of a building and what this efficiency actually is in practice.
Adding to this are questions related to ROI. Real estate owners can’t benchmark building performance to prior performance when starting from scratch. As fiduciaries to their own investors, real estate owners need an immediate and concrete ROI story, particularly for public market investors. Though they tout an obvious and ideal value proposition, some design and construction technologies remain relatively nascent as they seek to reimagine the “Built World” from the ground up.
Retrofitting
Retrofitting involves upgrading the energy performance of existing commercial buildings. Given the sizable commercial footprint already around us, the market potential is enormous. Take for instance that more than 90% of the buildings in New York today will still be standing in 2050, and nearly 70% of the city’s total carbon emissions come from buildings.
As demolishing even a fraction of these buildings is not an option, retrofitting has emerged as a viable alternative. The option to retrofit only becomes more important when understanding that New York state has specifically targeted buildings as key components of its roadmap to cut carbon emissions by 85% by 2050.
In this endeavor, the estimated cost of bringing all buildings in New York into compliance is $20 billion. This is just commercial property in New York alone.
Measuring and monitoring
Following building upgrades during design, construction or after building operation comes the ongoing carbon monitoring and maintenance of physical assets.
Solutions such as Measurabl or Metrikus are now assisting the real estate industry in data collection, assessment of physical climate risk, and in providing educated decisions on how to best decarbonize. Coming into play here are substantive insights on a building’s performance that can be used to inform where to best allocate financial resources to optimize for efficiency.
While this type of tech may provide a seemingly easy path to carbon reduction, many solutions stop after collecting and organizing the data. This can often leave the real estate industry without actionable next steps to truly decarbonize. This final but integral impact assessment piece is perhaps the most important and biggest differentiator for many of these technologies.
But there’s a way ahead
While misperceptions are beginning to fade away around the ROI of climate software for real estate owners, hesitation around ROI still lingers within the venture community.
Despite increasing expenditure and adoption by real estate investment trusts (REITs), of the $60 billion invested in climate tech, only $3.7 billion went toward solutions for the built environment, per a recent PwC analysis of global VC investment trends. This number was the smallest of the five categories studied despite its outsized impact on global greenhouse gas emissions.
This could be due to a host of factors, including traditional questions around the capital efficiency of climate tech, ROI and the time to exit for venture investors.
But a deeper dive into a sample of public companies indicates these perceptions aren’t as real as one would imagine. Notably, data between a subset of software and climate tech companies surfaces a few surprising conclusions.
Despite selecting similar profiles for control4, climate tech companies in this sample not only raised less capital to achieve their revenue scale — by a factor of over two times — but generated more cash flow. This may speak to the notion that while climate technologies are often more capital-intensive than their traditional software peers at first, they often make for more scalable growth post-commercialization due to the inherent strength of the IP and product offering.
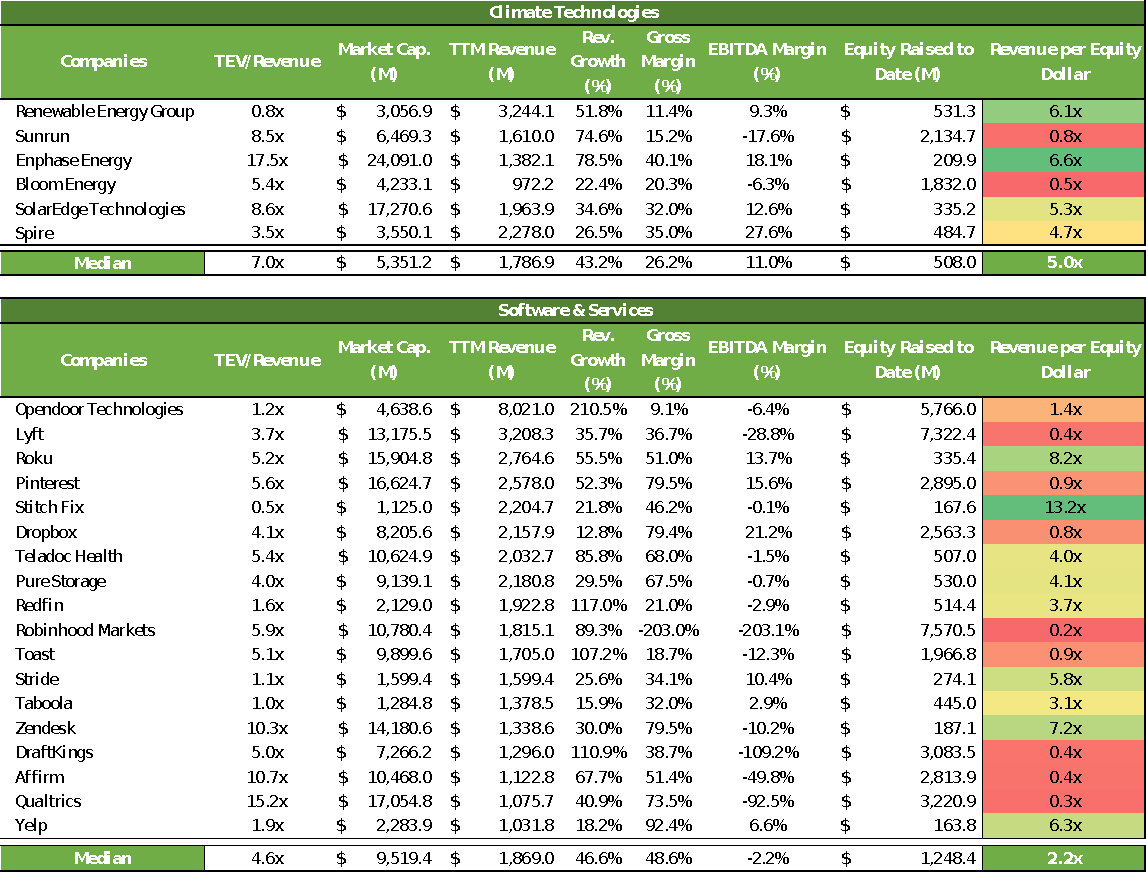
Climate technologies versus broader software and services: Revenue generated per invested equity. 4Control factors include: (1) Previous venture backing, (2) founded between 2000–2015, (3) at least $1 billion in revenue, (4) market capitalization between $1 billion and $20 billion. Financial metrics and market trading as of March 10, 2022. Note: “Equity Raised” calculated as private and public equity raised per PitchBook. Sources: PitchBook, CapIQ. Image Credits: SVB Capital
Taking a step back, this small sample size by no means indicates a “Buy” rating on climate tech versus all other software. Neither does it conclude that climate technology as a whole is more attractive, or even more capital efficient. Rather it indicates that myths surrounding the entire climate tech sector about its capital inefficiency or return profile are not necessarily true.
This means proof points exist for underwriting investment in this large, growing and greenfield category. For real estate owners, this adds to the compounding notion of the substantive ROI and that these technologies are here to stay. For founders, there might be hope for access to the lucrative term sheets and valuations traditionally playing out for other software startups
A change is coming
To be clear, the real estate industry has been making some moves. 58% of respondents to a Nareit Member Survey said they have already reduced their year-over-year GHG emissions, and 53% of these reduced their GHG emissions by 5% to 20%.
Simultaneously, a growing number of REITs, including industry leaders Prologis, Host, Kilroy and Avalonbay Communities have developed in-house climate targets. The rate of adoption shows, too — blue chip logos such as Salesforce, BlackRock and even Major League Baseball all crowd the websites of climate tech startups such as Measurabl, Passive Logic and Cove.Tool in a marked representation of the changing times.
For industry stakeholders who have been slow to adopt, the potential to unlock substantial cash flow and a clear ROI value proposition might lift lingering hesitation. This notion is generally supported by recent research from E&Y that signals cost and perceived lack of ROI are major considerations in delayed adoption among corporate real estate. Bringing this home is additional research from E&Y saying commercial real estate ranks more efficient operations and access to ESG data points as the #1 and #3 technology priorities in recent years.
A change is coming, and a paradigm might shift for REITs acting as managers of physical assets to custodians of global carbon impact. This notion may only continue to escalate with a clear ROI, changing priorities for constituents across the value chain and capital to drive these technologies forward.
Do look up, and all around
The market is there, the solutions are emerging and as the world changes before our eyes, it’s time to adapt or fall by the wayside. The answer may not be as chaotic and confusing as it seems. Perhaps the answers lie right before us, around us — where we live and where we work. And in the process of saving our world as we know it, we may just incite a technological revolution in the very asset class it is benefiting.
Disclaimer: Views are the author’s own and may not reflect those of SVB Capital.
