Over the last few years, cloud computing has grown more expensive than ever. Initially drawn to the promise of cutting costs on infrastructure spend, companies far and wide flocked to behemoths like AWS and Google Cloud to host their services. Technical teams were told this would reduce engineering costs and increase developer productivity, and in some cases it did.
Fundamental shifts in AI/ML were made possible by the ability to batch jobs and run them in parallel in the cloud. This reduced the amount of time it took to train certain types of models and led to faster innovation cycles. Another example was the shift in how software is actually architected: from monolithic applications running on VMs to a microservices and container-based infrastructure paradigm.
Yet, while the adoption of the cloud fundamentally changed how we build, manage and run technology products, it also led to an unforeseen consequence: runaway cloud costs.
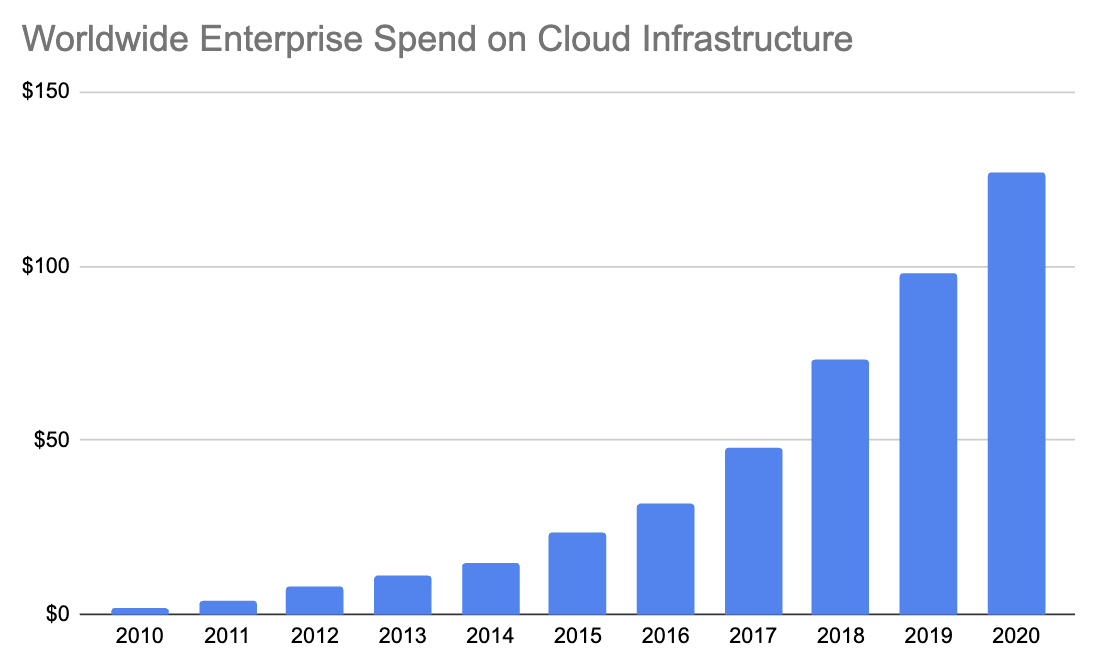
Total enterprise spend in billions. Numbers are approximated based on data from Synergy Research Group. Image Credits: Chelsea Goddard
While the promise of spending less spurred companies to migrate services to the cloud, many teams didn’t know how to do this efficiently and, by extension, cost-effectively. This created the first up-front investment opportunity we have seen behind the recent surge in venture funding to cloud observability platforms like Chronosphere ($255 million), Observe ($70 million) and Cribl ($150 million).
The basic thesis here is simple: If we provide visibility into what services cost, we can help teams reduce their spend. We can liken this to the age-old adage that goes something like, “You cannot change what you cannot see.” This has also been the primary driver for larger companies acquiring smaller observability players: to reduce the risk of churn by baiting customers with additional observability features, then increase their average contract value (ACV).
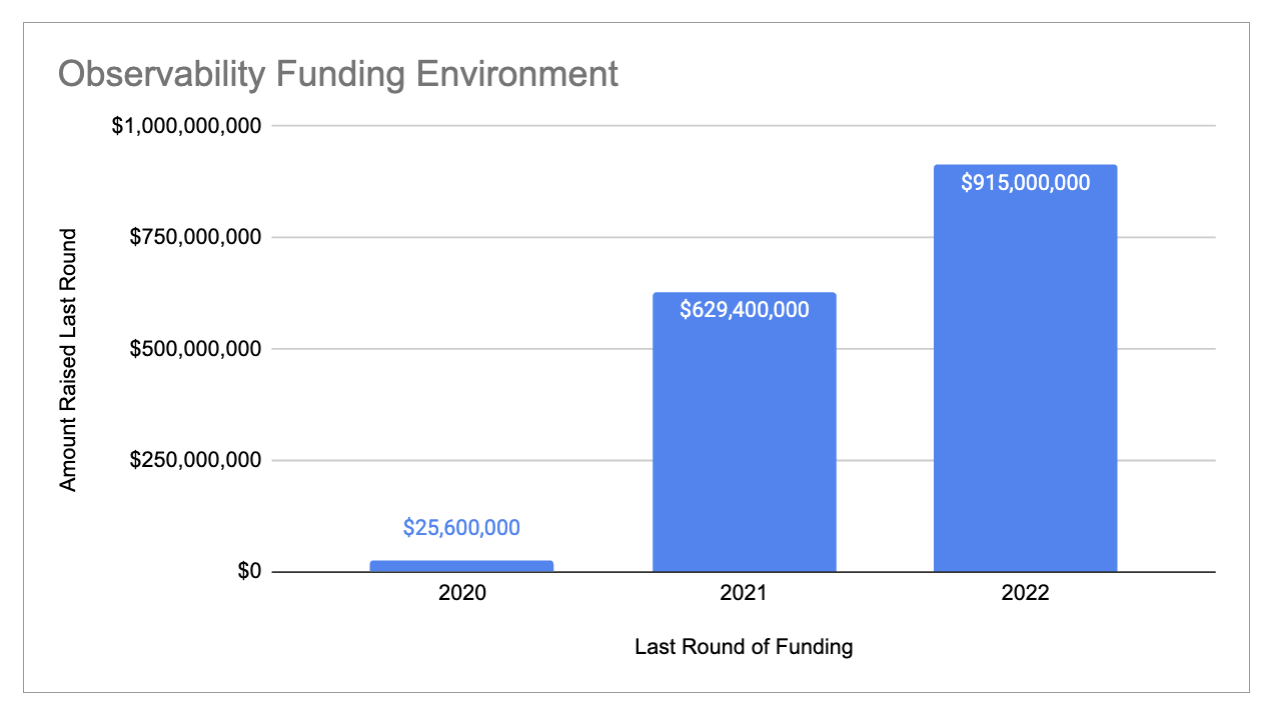
Sample of cloud observability funding landscape. See data here. Image Credits: Chelsea Goddard
The current market bodes well for observability product offerings. According to Flexera’s State of the Cloud Report, “roughly 77% of IT professionals with more than $2 million in cloud costs said they were surprised by how much they spent [on cloud costs].” We have also read that “70% of companies using the cloud plan to increase their budgets in the [near] future.”
The opportunity for venture-backed startups is clear, with strong demand, increasing competition and chances of a billion-dollar exit. However, it also implies the byproduct of having too many tools to choose from: analysis paralysis.
Yet, interestingly enough, product fatigue does not mean the problem has been solved. Instead, it points to a clear need for observability platforms that go a step beyond monitoring. This is precisely why optimization tools will be the next wave of product innovation for companies thinking about cloud infrastructure best practices.
Monitoring tools largely don’t offer optimization. Technical features like visibility, chargeback and allocations give users insight to help lower costs, but they do not optimize or automate where you need to focus efforts or reallocate resources to lower costs and increase efficiency. That is why optimization is the top cloud initiative, per survey respondents in Flexera’s report.
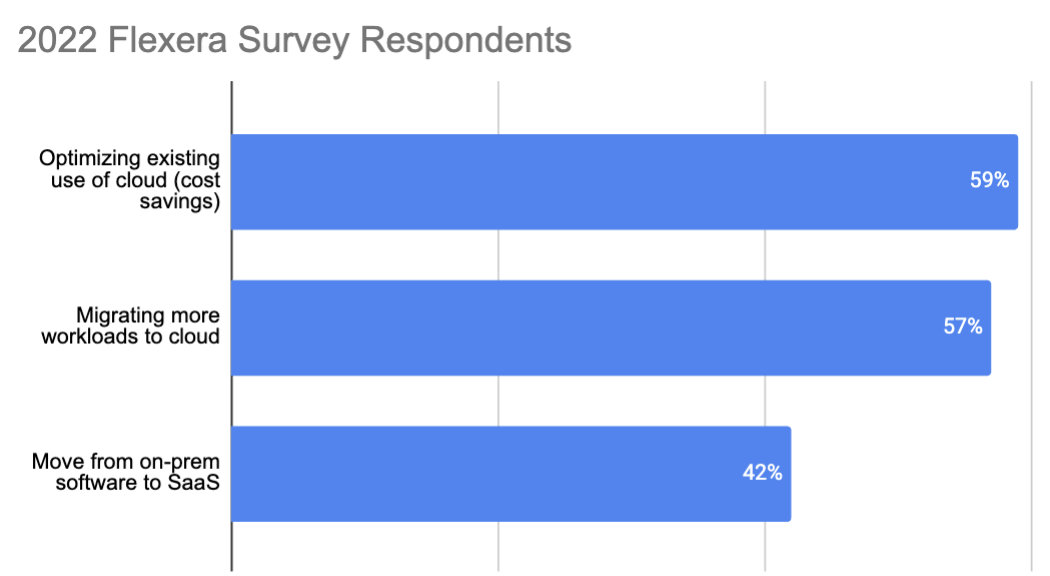
Optimizing existing use of cloud (cost savings) is top cloud initiative. Data sourced from Flexera 2022 Cloud Spend Report. Image Credits: Chelsea Goddard
Engineering managers face another problem — the bespoke approach to solving large-scale, combinatorial optimization problems. This reminds me of how companies used to solve payments before Stripe, or messaging before Twilio. Every company’s engineering team stood up a unique solution to a common problem. Once there was an easy-to-use developer choice, this painful process was happily outsourced to the companies we know and trust today.
This leads to the crux of my thesis: Once we are past this wave of cloud and edge initiatives, infrastructure investment will shift toward the next set of strategic enterprise priorities, automation and optimization. Further, developer tooling that enables customers to cut costs and increase responsiveness are particularly well positioned to win.
Another, more controversial, opinion is that while in other sectors, point solutions can be limited to capturing a market, in the optimization space you actually want something that looks like a point solution. This is because large enterprise organizations like Apple and Google have already spent millions of dollars setting up their own observability platforms. While they are unlikely to outsource all of their observability spend, they are likely to outsource their optimization and automation spend. In fact, we should assume that for more cloud-forward companies, this is already a top priority.
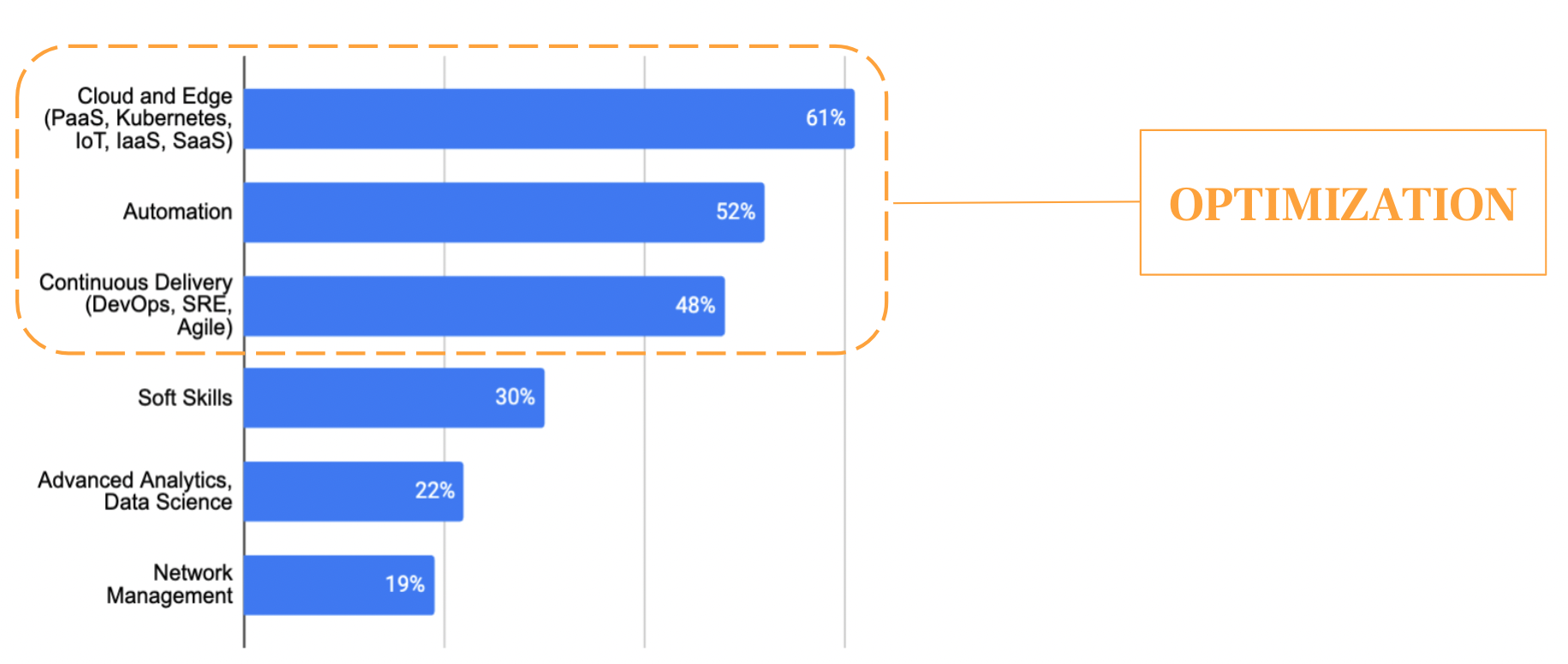
Top three categories of investment expected to increase are all linked to optimization. Image Credits: Chelsea Goddard
Sync Computing, which recently raised a Series A, is an excellent example of a startup well positioned to win in this new paradigm. It helps engineering teams programmatically optimize their cloud configurations, resulting in lower cloud costs. Recently, Sync announced an “Autotuner API,” which will enable developers to generate a prediction of “optimized recommendations for their Spark job running on AWS or Databricks.” As the market matures, we should expect to see more observability incumbents launch optimization features that directly integrate with solutions like Sync.
In conclusion, optimization is the next big thing in cloud management, because organizations will continue to look for ways to cut costs, and optimization tooling offers a clear solution. As cloud infrastructure best practices mature, engineering managers will vie for their team to adhere to industry standards that combine automation and optimization workflows.
Further, the growing adoption of machine learning means companies will continue to run large and expensive jobs in the cloud, mostly for faster recommendations (at the consumer level) and response times (at the product level). This will require proactive recommendations (optimization), not just reactive alerting (observability).
Lastly, optimization, unlike observability, has a low barrier to adoption for large and small companies alike. This places optimization tools at the center of the spotlight.
Disclaimer: The thoughts and opinions expressed in this article were authored independently of Sync Computing and Space Capital, and only represent the views of the author.
