Does it really take an average of seven to eight years for a successful startup to exit? What can early-stage founders do to accelerate outcomes?
We wanted to know if founding teams can execute faster with a higher degree of success if they’re able to take advantage of relevant executive expertise. After all, that’s the thesis we built our venture model around — we purposefully designed M13 so that early-stage founders get access to experienced executives they wouldn’t otherwise have the money to hire or the time to vet, onboard and manage.
Even if companies are doing everything right, they still reduce time to exit when they have multiple founders with prior relevant experience as a senior leader or operator.
We looked at years of data from hundreds of successful startups. As it turns out, the impact of relevant executive expertise is even greater than we had anticipated — to the tune of doubling the rate of return on a venture investment.
When it comes to measuring leadership experience, information about an individual executive’s experience — for example, how long they’ve been an exec — is publicly available. Unfortunately, there isn’t readily available structured data around a founding team’s seniority and how early the founders bring on people with more experience as an operator or leader.
To find out if leadership experience significantly impacts startups’ success, we analyzed nearly 800 executives at more than 200 companies that reached a sizable exit (greater than or equal to a $500 million valuation) via an IPO on a U.S. exchange or an exit via M&A from 2004-2019. About 70% of the companies in our dataset exited between 2016-2019, including notable IPOs like Spotify, Zoom, Uber and Peloton. We decided to exclude companies in the biotech/life sciences space because these companies follow a different growth trajectory than consumer tech and B2B tech and traditionally exit via IPO or M&A at a much earlier stage.
Here’s what our analysis of startups with successful exits revealed.
Of successful exits, the average actually is 7-8 years
While there are other intangible variables for startup success, the basic equation is the time and capital required to achieve an exit and the size of that exit.
Our dataset validates the widely accepted statement that successful exits take about seven to eight years:
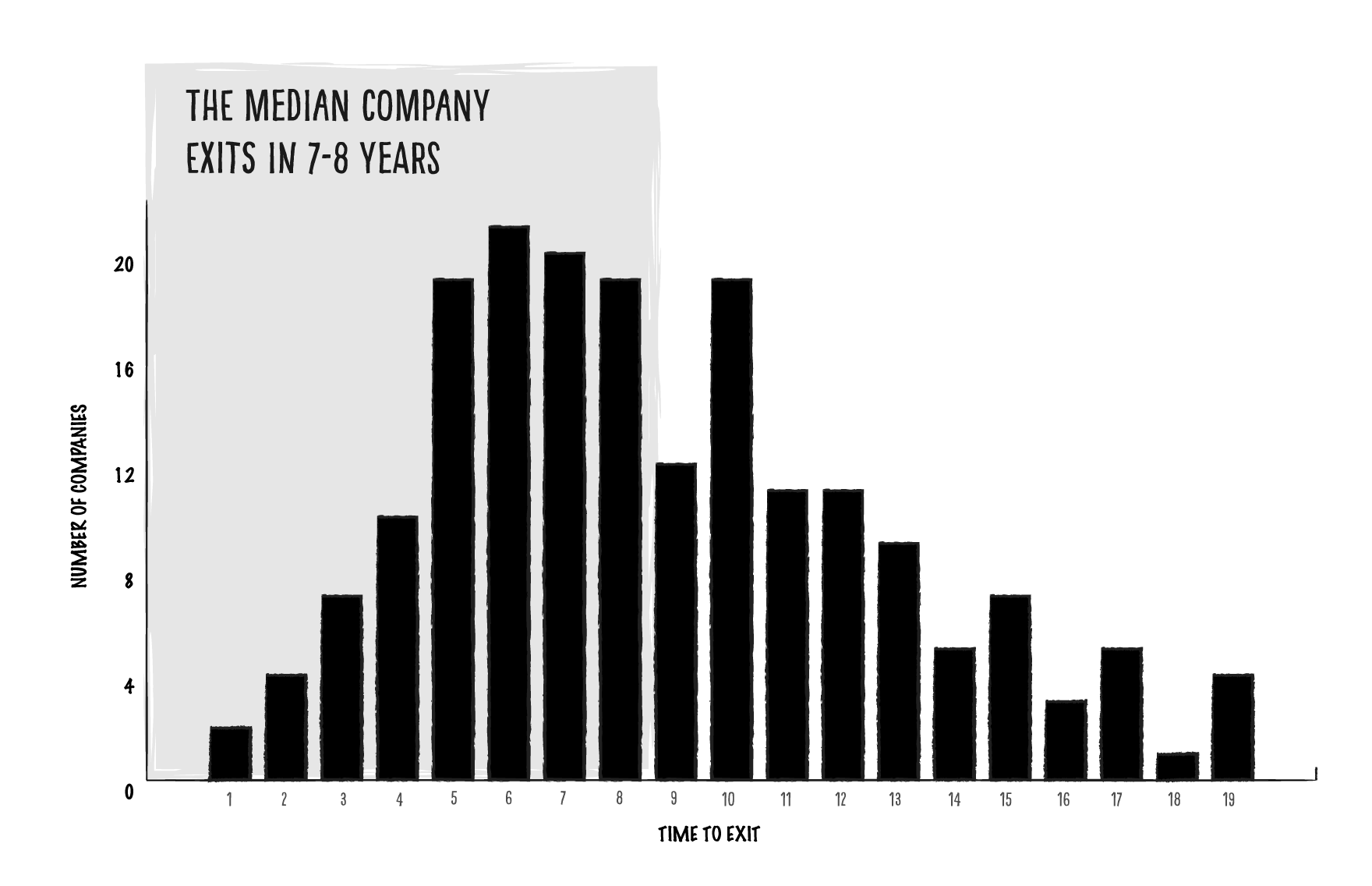
Image Credits: M13
But could a variable like relevant leadership experience actually accelerate the time to exit? We wondered: Beyond time and capital, are there any factors — like experience as a leader or operator — that can have an exponential impact on the exit outcome? And when is the right time for those human capital resources to be introduced to make that impact?
In terms of executive-level leadership, we limited our analysis to startups with successful exits and individuals in CEO, CFO, COO, CTO, CPO, CRO, CMO and CHRO roles (or comparable leadership titles). We then looked at those individuals’ prior relevant leadership experience, including how many years of post-grad experience these individuals have, how many companies they’ve worked at and which executive roles they’ve held in the past.
It turns out (less) time is (nearly double the) money
Our analysis of startups with successful exits found that companies with multiple founders who have prior relevant leadership experience will exit 33% faster — but this earlier exit is coupled with a finding that they will have also raised 34% less capital. Combined, these two improvements can nearly double an investor’s rate of return.
According to our analysis, if a company achieves a $500 million exit in 4.7 years (or 33% faster than the average of seven years) and if they exit having raised 34% less capital — the theoretical IRR for a Series A lead investor ($10 million check for 15% starting ownership) improves by 81%:
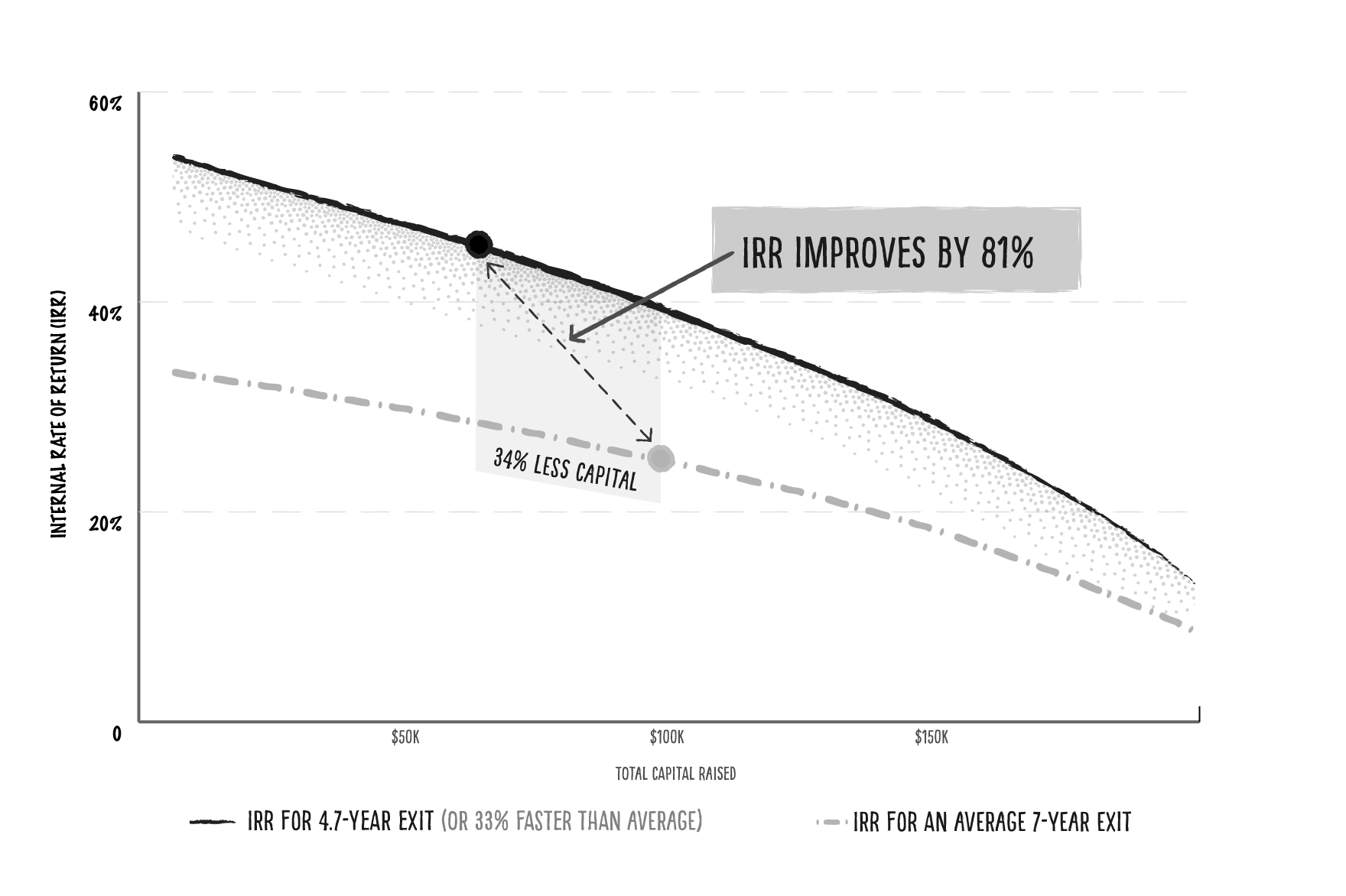
Image Credits: M13
Companies can exit 33% faster by adding people with leadership experience early
Our analysis of startups with successful exits shows that companies with at most one founder with executive experience exit in 9.6 years on average.
In comparison, companies with two or more founders with executive experience tend to exit in 6.4 years (33% faster).
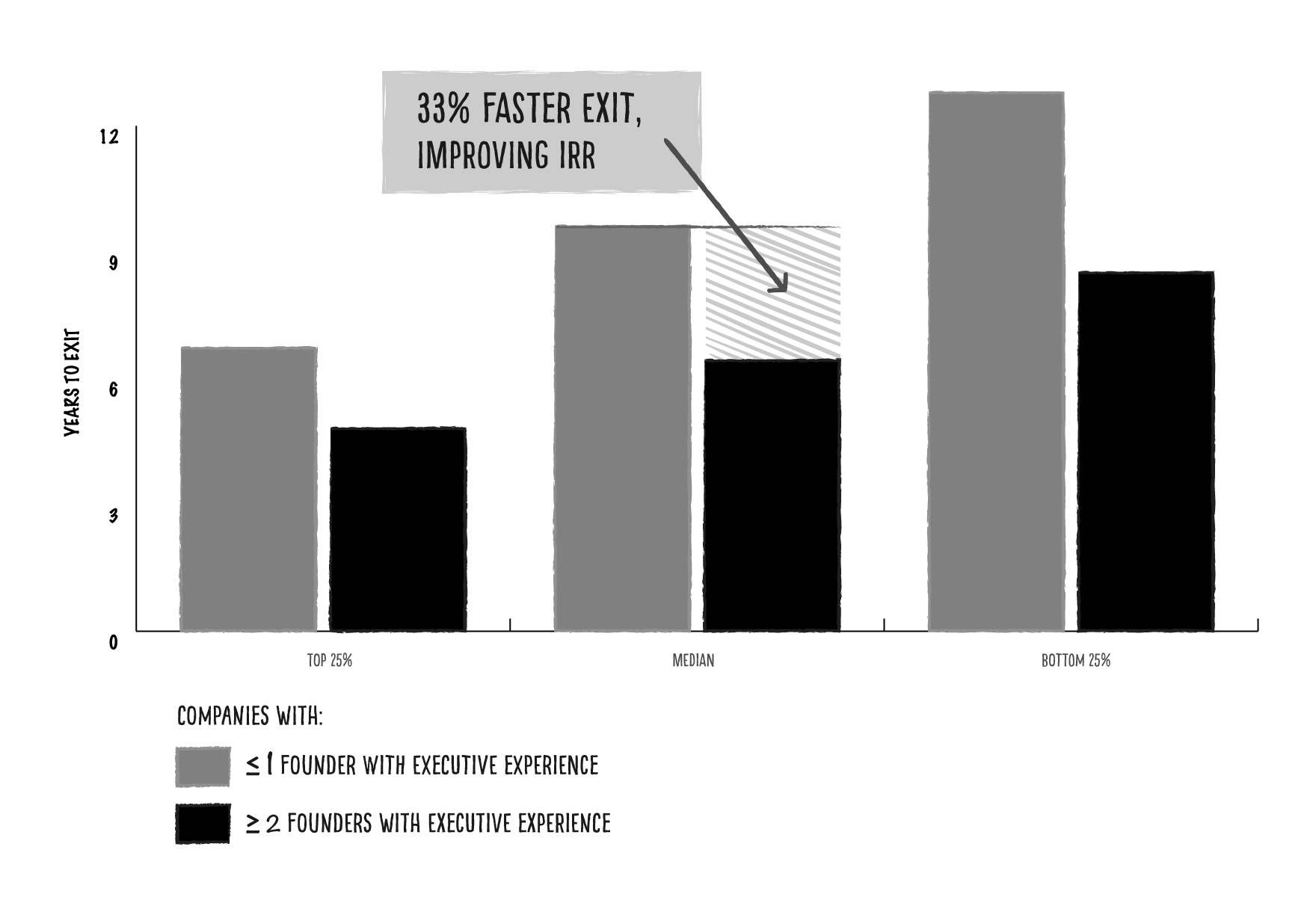
Image Credits: M13
What this means: Even if companies are doing everything right — in other words, they’re in the top 25% of our dataset (in terms of exit speed) with great founders, high-performing teams, a booming market and flawless execution — they still reduce time to exit when they have multiple founders with prior relevant experience as a senior leader or operator.
Not only do companies with seasoned founders exit faster, they also need to raise 34% less capital before exit, boosting IRR
If companies already have great founders, high-performing teams, a booming market and flawless execution, we found that layering on some prior relevant leadership experience early also allows that company to exit having raised less capital — and with less dilution.
We found that it takes an average of seven to eight years for a company to exit after five to six funding rounds (with outliers). On average, these companies will have raised $386 million, including exit.
Successful companies with founders who have executive experience not only exit 33% faster, but they also raise 34% less capital before exit, further improving IRR.
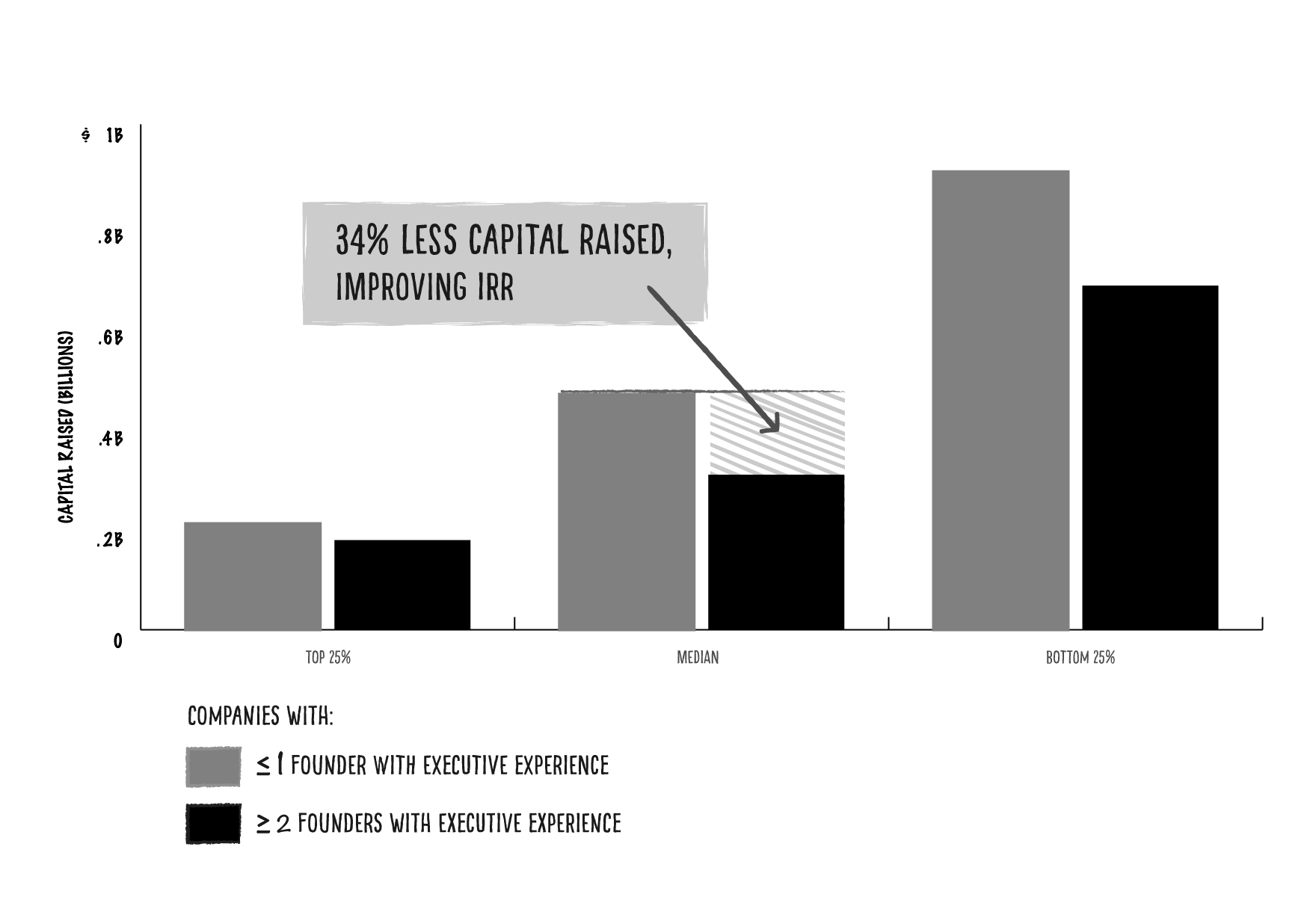
Image Credits: M13
Companies with little executive experience tend to exit having raised $466 million in funding. In comparison, companies with multiple founders with executive experience tend to exit having raised $306 million in funding.
There’s still room for companies to benefit from adding relevant leadership experience early
Although companies realize the need for prior relevant leadership experience, our analysis of startups with successful exits found that they tend to gradually build their executive team.
According to our data, these companies tend to ramp up C-level hiring linearly into IPO, no matter their size or their executive teams’ collective experience. Four years before exit, on average, these companies have only 43% of the shared executive experience they will eventually have when they exit. Even successful companies that start with the most executive experience still tend to add experience at the same rate.
We believe this data not only supports M13’s venture model, but it can help guide the decision to prioritize hiring seasoned executives. Executive experience allows companies to identify common pitfalls and hurdles proactively, see around corners, and apply common frameworks and practices. In turn, this helps companies save so much time.
Methodology: We used publicly available information from Crunchbase, PitchBook, LinkedIn and various news publications to look at 783 executives from 201 companies that reached IPO or exited via M&A between 2004 and 2019. Our dataset includes U.S. stock exchange listings only (Nasdaq and NYSE) from various industries, excluding biotech/life sciences. We looked at 112 small-sized companies with an IPO valuation of $500 million to $2 billion, 73 medium-sized companies with an IPO valuation of $2.1 billion to $9.2 billion, and 16 large-sized companies with an IPO valuation of $11 billion to $82 billion.
